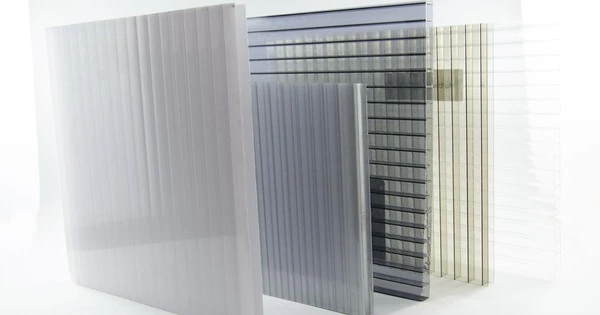
Polycarbonates (PC) are a class of thermoplastic polymers with carbonate groups in their chemical structures. This is a class of thermoplastic polymers noted for its outstanding strength, clarity, and impact resistance. Polycarbonates lack a unique resin identification code (RIC) and are classified as “Other,” number 7 on the RIC list. Polycarbonate products may include the precursor monomer bisphenol A (BPA).
Here are some key aspects of polycarbonates:
- Chemical Structure: In their polymer chain, these are made up of repeated carbonate groups (-O-CO-O-). Bisphenol A Polycarbonate (PC) is the most prevalent form of polycarbonate made from bisphenol-A (BPA).
- Transparency: These are exceedingly translucent, much like glass. Because of their transparency, as well as their exceptional optical qualities, they are appropriate for applications requiring visibility and clarity, such as eyeglass lenses, optical discs, and transparent protective barriers.
- High Impact Resistance: One of the most remarkable characteristics of polycarbonates is their high impact resistance. They can endure a great lot of physical damage without shattering, making them excellent for use in safety glasses, face shields, helmets, and bulletproof windows.
- Thermal Stability: Polycarbonates have good thermal stability and can typically withstand temperatures between -40°C to 130°C (-40°F to 266°F) without significant deformation or degradation. Some modified polycarbonates can handle even higher temperatures.
- Dimensional Stability: They exhibit good dimensional stability, meaning they maintain their shape and size over a wide range of temperatures and under load, which is important in applications such as automotive parts and electronic components.
- Ease of Processing: Polycarbonates can be easily molded and formed into various shapes using common plastics processing techniques like injection molding, extrusion, and thermoforming.
Chemical Resistance
They are resistant to many substances, yet some solvents and chemicals can impact them at high temperatures. Because they are excellent electrical insulators, they are appropriate for electrical and electronic components.
While polycarbonates are naturally resistant to UV radiation, extended exposure to sunlight can cause them to disintegrate. UV stabilizers are frequently used to improve outdoor performance. These can be recycled, although there are certain complications due to the presence of BPA in some formulations. For increased recyclability, efforts have been made to manufacture BPA-free polycarbonates.
Common applications
Polycarbonates are strong, durable materials that are optically transparent in some grades. They are simple to work with, mold, and thermoform. Polycarbonates have a wide range of uses because to their characteristics. Because of their unique combination of features, they are extensively employed in a wide range of applications. Common applications of polycarbonates include:
- Eyewear: Sunglasses and prescription glasses lenses.
- Automotive: Interior components, headlamp lenses, and safety features.
- Electronics: CD/DVD discs, computer and smartphone housings.
- Construction: Skylights, roofing, and safety glazing.
- Medical: Medical devices and equipment, such as incubators and syringe barrels.
- Aerospace: Aircraft windows and components.
- Security: Bulletproof glass and riot shields.
- Consumer Goods: Water bottles, food containers, and kitchenware.