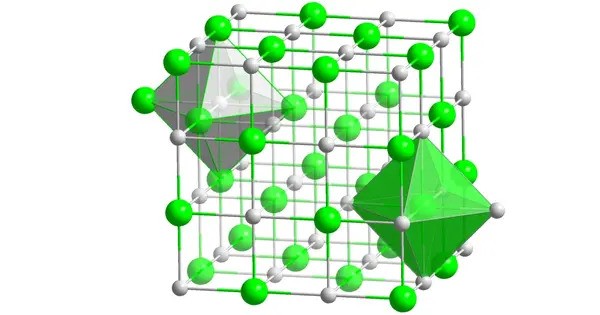
Plutonium selenide is a binary inorganic compound of plutonium and selenium with the chemical formula PuSe. The compound forms black crystals and does not dissolve in water. It is typically crystallizes in the rock salt structure, which is common among binary chalcogenides of actinides. It generally appears as a black or dark-colored solid.
Plutonium selenide can be synthesized through direct combination of plutonium and selenium elements at high temperatures, or through chemical vapor deposition methods. Both plutonium and selenium compounds can be toxic. Plutonium is a heavy metal with significant radiological hazards, and selenium compounds can be toxic at certain concentrations.
Properties
- Chemical formula: PuSe
- Molar mass: 323.024
- Appearance: Black crystals
- Melting point: 2,075 °C (3,767 °F; 2,348 K)
- Solubility in water: insoluble
Crystal Structure
Plutonium selenide often crystallizes in a face-centered cubic (FCC) structure similar to NaCl. It is thermally stable at high temperatures. As a compound containing plutonium, PuSe is highly radioactive and requires careful handling and storage.
Preparation
Plutonium selenide can be synthesized by directly combining plutonium and selenium:
Pu + Se → PuSe
Pu+Se→PuSe
This reaction is usually carried out in a controlled environment to prevent contamination and exposure to radioactivity.
Applications
- Nuclear Technology: Due to its radioactive properties, plutonium selenide has potential applications in the field of nuclear technology, particularly in the development of advanced nuclear fuels and radioactive sources.
- Thermoelectric Materials: Plutonium selenide, like other actinide compounds, has been studied for its potential use in thermoelectric devices, which convert heat into electricity.
- Research: PuSe is of interest in solid-state physics and materials science research, particularly in the study of actinide compounds and their unique electronic and magnetic properties.
Safety Considerations
Handling plutonium selenide requires strict safety protocols due to the radiotoxicity of plutonium. Appropriate shielding, containment, and disposal methods are essential to prevent radiation exposure and environmental contamination.