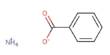
Almarudite is an extremely rare alkaline manganese beryllium silicate mineral of the cyclosilicates (ring silicates) class, with the formula written as K([], Na)2 (Mn2+, Fe2+, Mg)2 (Be,Al)3[Si12O30], from the volcanic environment of the Eifel Mountains, Germany.
Almarudite is a hexagonal-dihexagonal dipyramidal mineral containing aluminum, beryllium, calcium, iron, magnesium, manganese, oxygen, potassium, silicon, sodium, and zinc.
General information:
- Hardness: 6
- Specific Gravity: 2.71
- Crystal System: Hexagonal
- Member of: Osumilite Group
- Tenacity: Brittle
- Density: 2.71 g/cm3 (Measured)
They are embedded in a carbonate-quartz matrix and are associated with ettringite/thaumasite, mayenite, cuspidine, larnite, “calcio-olivine”, tobermorite, portlandite, hydrocalumite, a member of the ellestadite series, magnetite and hematite.

Physical Properties of Almarudite
Almarudite has been found in a single silicate-rich xenolith. It forms euhedral, platy crystals flattened on {0001}, with a maximum diameter of about 1.5 mm and a maximum thickness of 0.2 mm. It is associated with tridymite, sanidine, “clinopyroxene”, “amphibole”, quartz, hematite, sillimanite and rare braunite. Almarudite is yellow to orange, with a light orange streak and vitreous luster.
- Cleavage: None
- Color: Yellow, Orange.
- Diaphaneity: Transparent
- Fracture: Brittle – Irregular – Very brittle fracture producing irregular fragments
- Habit: Euhedral Crystals – Occurs as well-formed crystals showing good external form.
- Habit: Tabular – Form dimensions are thin in one direction.
- Luster: Vitreous (Glassy)
- Streak: light orange
Information Source;