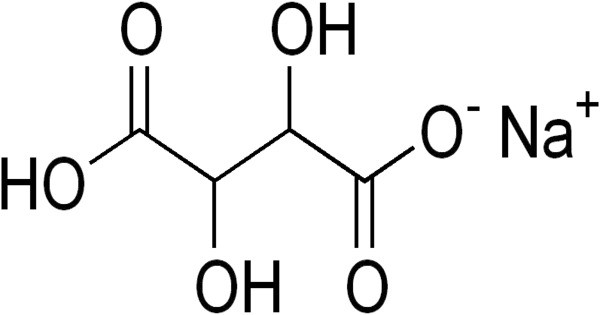
Monosodium tartrate or sodium bitartrate is a sodium acid salt of tartaric acid. Its chemical formula is NaHC₄H₄O₆. As a food additive it is used as an acidity regulator and is known by the E number E335. As an analytical reagent, it can be used in a test for ammonium cation which gives a white precipitate. It appears as a white, crystalline powder and is soluble in water.
It helps maintain the stability and appearance of processed foods by binding metal ions. It is also used in pharmaceuticals and occasionally in chemical analysis. While generally recognized as safe when consumed in small quantities, excessive intake may lead to mild gastrointestinal irritation. It should be stored in a cool, dry place away from moisture.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C4H5NaO6
- Molar mass: 172.07 g/mol
- Appearance: White crystalline powder
- Solubility: Soluble in water; slightly soluble in alcohol
- Melting Point: Decomposes before melting
- pH (1% solution): Slightly acidic, typically around 3–5
- Stability: Stable under normal conditions; incompatible with strong oxidizers
- Form: Crystalline solid
- Taste: Slightly acidic or sour
- Odor: Odorless
- Solubility in Water: High
Natural Occurrence
Monosodium tartrate does not occur freely in nature in large amounts but is derived from tartaric acid, which occurs naturally in:
- Grapes
- Bananas
- Tamarinds
- Wine sediments (as cream of tartar or potassium bitartrate)
Monosodium tartrate is generally synthetically prepared from tartaric acid and sodium compounds (like sodium carbonate or sodium hydroxide).
Uses and Applications
- Food Additive (E335(i)): Used as an acidity regulator, antioxidant, and emulsifier. Common in jellies, baked goods, soft drinks
- Laboratory Use: Sometimes used in Fehling’s solution preparation (though sodium potassium tartrate is more common)
- Buffering Agent: Helps stabilize pH in pharmaceuticals or food systems