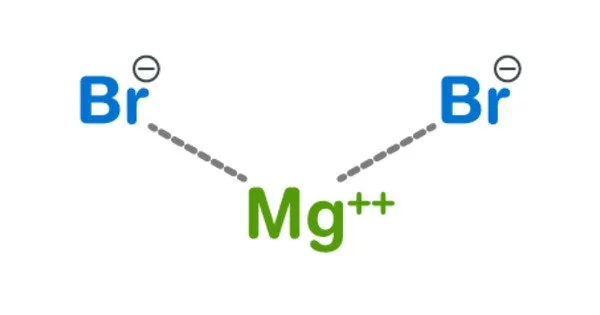
Magnesium bromide are inorganic compounds with the chemical formula MgBr2(H2O)x, where x can range from 0 to 9. It is a white, crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water. Magnesium bromide is often used in the preparation of other magnesium compounds and as a catalyst in certain chemical reactions. They are all white deliquescent solids.
Magnesium bromide is typically found as a white, crystalline solid at room temperature. It can also appear as a colorless or white powder when in a dry form. Some magnesium bromides have been found naturally as rare minerals such as: bischofite and carnallite.
Properties
- Chemical formula: MgBr2 (anhydrous), MgBr2·6H2O (hexahydrate)
- Molar mass: 184.113 g/mol (anhydrous), 292.204 g/mol (hexahydrate)
- Appearance: white hygroscopic hexagonal crystals (anhydrous), colorless monoclinic crystals (hexahydrate)
- Density: 3.72 g/cm3 (anhydrous), 2.07 g/cm3 (hexahydrate)
- Melting point: 711 °C (1,312 °F; 984 K) 172.4 °C, decomposes (hexahydrate)
- Boiling point: 1,250 °C (2,280 °F; 1,520 K)
- Solubility in water: 102 g/(100 mL) (anhydrous), 316 g/(100 mL) (0 °C, hexahydrate)
- Solubility: ethanol: 6.9 g/(100 mL), methanol: 21.8 g/(100 mL)
Synthesis
Magnesium bromide can be synthesized by treating magnesium oxide (and related basic salts) with hydrobromic acid. It can also be made by reacting magnesium carbonate and hydrobromic acids, and collecting the solid left after evaporation.
As suggested by its easy conversion to various hydrates, anhydrous MgBr2 is a Lewis acid. In the coordination polymer with the formula MgBr2(dioxane)2, Mg2+ adopts an octahedral geometry.
Natural Occurrences
Magnesium bromide occurs naturally in sea water in small amounts. It is usually found as part of the dissolved salts in the ocean. It is sometimes found in brine solutions in salt lakes and some mineral deposits, though it is less abundant than other magnesium salts like magnesium chloride.
Extraction
Magnesium bromide can be obtained through the reaction of magnesium carbonate (MgCO₃) or magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)₂) with hydrobromic acid (HBr), or by reacting magnesium metal with bromine gas. It can also be synthesized in laboratories and industries using methods that involve magnesium and bromine-containing compounds.
Synthetic Occurrences
It is frequently used in industrial processes, especially in the production of magnesium metal and as a fluxing agent in metal refining. It is used in the preparation of certain pharmaceutical and chemical reagents.
Uses and reactions
- Magnesium bromide is used as a Lewis acid catalyst in some organic synthesis, e.g., in aldol reaction.
- Magnesium bromide also has been used as a tranquilizer and as an anticonvulsant for treatment of nervous disorders.
- Magnesium bromide modifies the catalytic properties of palladium on charcoal.
- Magnesium bromide hexahydrate has properties as a flame retardant.
- Treatment of magnesium bromide with chlorine gives magnesium chloride. This reaction is employed in the production of magnesium chloride from brines.