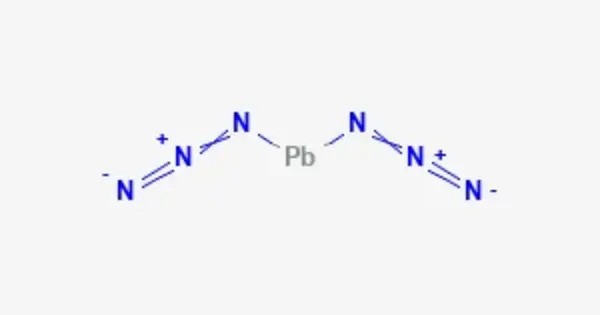
Lead(II) azide Pb(N3)2 is an inorganic compound. More so than other azides, it is explosive. It is a highly sensitive and powerful explosive compound. It is used in detonators to initiate secondary explosives. In a commercially usable form, it is a white to buff powder. It is also used in detonators, blasting caps, and other explosive devices due to its ability to decompose rapidly and release a large amount of energy upon initiation.
Properties
It is typically appears as a white or colorless crystalline solid. It is insoluble in water but can dissolve in some organic solvents. It is unstable and highly sensitive to shock, heat, friction, or impact. It can decompose easily, releasing nitrogen gas (N₂) and other products.
- Chemical formula: Pb(N3)2
- Molar mass: 291.2 g·mol−1
- Appearance: White powder
- Density: 4.71 g/cm3
- Melting point: 190 °C (374 °F; 463 K) decomposes, explodes at 350 °C
- Solubility in water: 2.3 g/100 mL (18 °C), 9.0 g/100 mL (70 °C)
- Solubility: Very soluble in acetic acid
- Insoluble in ammonia solution, NH4OH
Preparation and handling
Lead(II) azide is prepared by the reaction of sodium azide and lead(II) nitrate in aqueous solution. Lead(II) acetate can also be used.
Thickeners such as dextrin or polyvinyl alcohol are often added to the solution to stabilize the precipitated product. In fact, it is normally shipped in a dextrinated solution that lowers its sensitivity.
Occurrences
Lead(II) Azide is not found naturally in significant amounts but can be synthesized in laboratories. Its most common uses are industrial:
- Explosives and Ammunition: It is used in detonators and as an initiating charge in military applications.
- Chemical Synthesis: It can also be employed in chemical laboratories for the synthesis of other compounds, particularly in the preparation of azides or as a reagent in some reactions.
Since it is a synthetic compound, it does not occur in nature like minerals but is instead produced industrially under controlled conditions due to its sensitivity and explosive nature.
Uses
Detonators: Because of its sensitivity to impact and heat, lead(II) azide is primarily used in detonators and explosive devices.
Blasting Caps: It is often incorporated in blasting caps, where a small trigger (such as heat or impact) will cause it to explode and trigger a larger explosive charge.
Safety Concerns
Lead(II) azide is toxic, and exposure to lead compounds can cause serious health issues such as lead poisoning. It is also a hazardous material due to its explosiveness. Proper handling and disposal are necessary when dealing with lead(II) azide in any capacity.