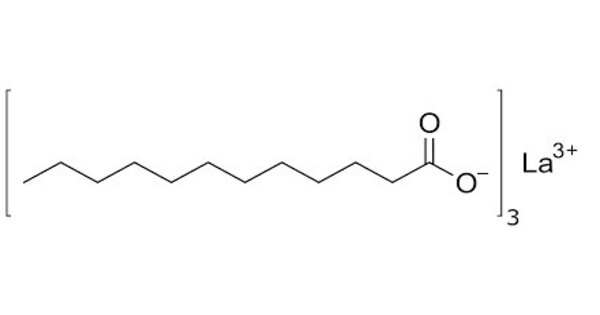
Lanthanum laurate is a metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C36H72LaO6. It is a compound composed of lanthanum, a rare earth metal, and lauric acid, which is a fatty acid. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid (lauric acid). In this compound, lanthanum typically forms a salt with lauric acid.
Lanthanum laurate is of interest in materials science and chemistry due to its potential applications in various fields, such as catalysis, materials synthesis, and possibly even in electronic or optical devices.
Properties
Lanthanum laurate can be stable under moderate temperatures but may decompose at high temperatures, releasing lauric acid and lanthanum oxides. It is generally insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents like ethanol or acetone. It may react with acids or bases, forming lanthanum salts or complexes.
- Chemical formula: C36H72LaO6
- Molar mass: 739.871 g·mol−1
- Solubility in water: Insoluble
Applications
- Catalysis: Lanthanum-based compounds can serve as catalysts in various chemical reactions. The inclusion of lauric acid may affect the compound’s catalytic properties.
- Material Science: Lanthanum compounds are investigated for their unique electronic and optical properties. Lanthanum laurate might be used in the development of materials with specific characteristics.
- Ceramics and Glasses: Lanthanum compounds are sometimes used in the formulation of advanced ceramics and glasses due to their high refractive indices and other desirable properties.