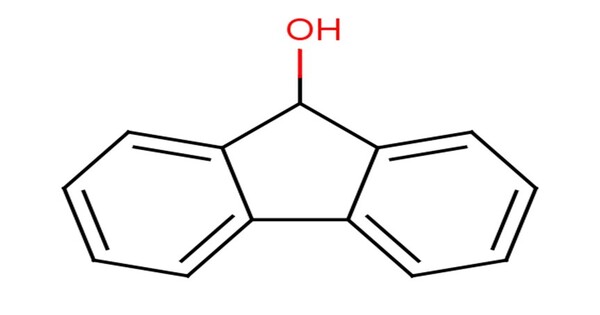
Fluorenol, also known as hydrafinil, is an alcohol derivative of fluorene. It is a compound derived from fluorene, a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon. In the most significant isomer, fluoren-9-ol or 9-hydroxyfluorene, the hydroxy group is located on the bridging carbon between the two benzene rings. It consists of a fluorene molecule with a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to one of its carbon atoms.
Hydroxyfluorene can be converted to fluorenone by oxidation. It is a white-cream colored solid at room temperature. This chemical compound has gained interest in scientific research due to its potential pharmacological properties, particularly as a potential treatment for alcohol dependence.
Properties
Fluorenol is sparingly soluble in water but soluble in organic solvents like ethanol, methanol, ether, and chloroform. It consists of a fluorene molecule with a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to one of its carbon atoms.
- Chemical formula: C13H10O
- Molar mass: 182.22 g/mol
- Appearance: Off-white crystalline powder
- Density: 1.151 g/mL
- Melting point: 152 to 155 °C (306 to 311 °F; 425 to 428 K)
- Solubility in water: Practically insoluble
Reactivity
The hydroxyl group in fluorenol makes it susceptible to various chemical reactions typical of alcohols, including oxidation and esterification reactions. It can undergo reactions such as dehydration to form fluorenone, or oxidation to form fluorenone or fluorenone derivatives.
Applications
Fluorenol and its derivatives find applications in organic synthesis, particularly in the production of pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. It has been studied for its potential as a pharmaceutical intermediate and as a precursor in the synthesis of various organic compounds.
Biological Activity
Research suggests potential biological activities of fluorenol derivatives, including antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anticancer properties, although further studies are necessary to fully understand and harness these activities.
Safety
As with any chemical compound, precautions should be taken when handling fluorenol. It should be handled in a well-ventilated area, and appropriate personal protective equipment should be worn. Detailed safety information, including toxicity data and handling procedures, can be found in Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) provided by chemical suppliers.
Toxicity
Fluorenol is toxic to aquatic organisms including algae, bacteria, and crustaceans. Fluorenol was patented as an insecticide in 1939, and is an algaecide against the green algae Dunaliella bioculata. Its toxicity and carcinogenicity in humans are unknown.