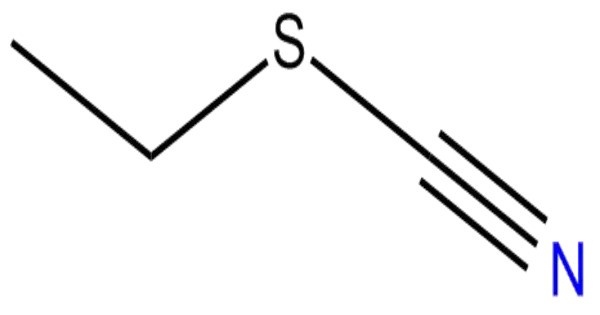
Ethyl thiocyanate is a chemical compound used as an agricultural insecticide. It is an organic compound with the molecular formula C3H5NS, belonging to the family of alkyl thiocyanates. It consists of an ethyl group (–C2H5) bonded to the thiocyanate functional group (–SCN). This compound typically appears as a colorless to pale liquid with a pungent odor, characteristic of many sulfur-containing organic substances.
In terms of stability, ethyl thiocyanate is relatively volatile and flammable, requiring careful handling and storage under controlled conditions. It may be irritating to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract, so protective equipment is recommended during laboratory use. Although not widely used on an industrial scale compared to other alkyl thiocyanates, its reactivity makes it valuable for specialized research applications in organic synthesis and chemical analysis.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C3H5NS
- Molar mass: 87.14 g/mol
- Appearance: Colorless to slightly yellow liquid
- Odor: Sharp, pungent, irritating smell
- Boiling point: Around 146–147 °C
- Density: ~1.0 g/cm³
- Solubility: Slightly soluble in water; more soluble in organic solvents like ethanol, ether, and chloroform
- Reactivity: Contains both sulfur and nitrogen, making it reactive in nucleophilic and electrophilic substitutions. It can hydrolyze slowly under moisture, producing ethyl mercaptan and other byproducts.
Occurrences
Ethyl thiocyanate is not naturally abundant but can be formed as a volatile compound in plants, especially in members of the Brassicaceae (mustard family) through the breakdown of glucosinolates. Trace amounts may also occur in some fermentation processes. Industrially, it is synthesized via reactions of ethyl halides with thiocyanate salts.
It is sometimes detected as a flavor or aroma compound in certain foods and beverages but is generally considered toxic at higher concentrations. In the laboratory, it finds limited use as an intermediate in organic synthesis and chemical research.
Application
Ethyl thiocyanate is primarily of interest in organic and medicinal chemistry, where it can serve as an intermediate for the synthesis of more complex molecules. Due to the reactive thiocyanate group, it participates in substitution and addition reactions, making it useful in preparing heterocycles, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals. It can also act as a reagent in studying the behavior of thiocyanate derivatives and sulfur–nitrogen chemistry.