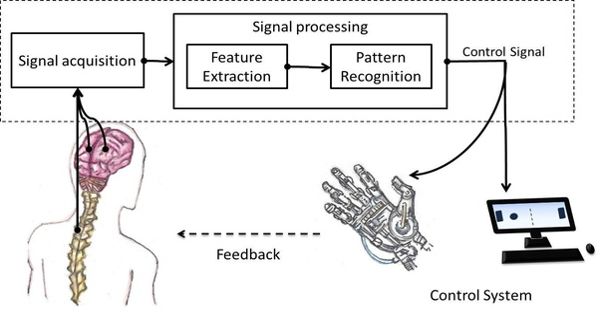
Electronic publishing (also known as digital publishing or online publishing) encompasses the digital publication of e-books, digital magazines, and the creation of digital libraries and catalogues. It is the process of creating and disseminating textual or visual information in digital format rather than traditional print media. It also involves the editing of books, journals, and magazines for display on a screen (computer, e-reader, tablet, or smartphone).
With the rise of the internet and digital technology, electronic publishing has grown in popularity and reach. It includes a wide range of digital products, such as books, periodicals, newspapers, academic journals, pamphlets, and many sorts of internet content.
About
Electronic publication has grown prevalent in scientific publishing, with some claiming that peer-reviewed scientific journals are being phased out in favor of electronic publishing. It is also becoming more usual to send books, periodicals, and newspapers to consumers via tablet reading devices, a market that is expanding by millions of dollars each year, thanks to online suppliers such as Apple’s iTunes bookstore, Amazon’s Kindle bookstore, and books in the Google Play Bookstore.
According to market studies, half of all magazine and newspaper circulation will be delivered digitally by the end of 2015, and half of all reading in the United States will be done without paper by 2015.
Here are some key aspects and components of electronic publishing:
- Digital Formats: PDF, EPUB (Electronic Publication), MOBI, HTML, and other digital formats are commonly used for electronic publications. These formats enable access to material on a wide range of devices, including e-readers, tablets, smartphones, and PCs.
- Online Distribution: The internet is frequently used to disseminate and access electronic publications. Websites, online markets (such as Amazon Kindle Store), email subscriptions, or downloadable files from a publisher’s website can all be used.
- Enhanced Content: Multimedia elements such as hyperlinks, music, video, and interactive features can be included in electronic publication. This improves the reader’s experience and interaction with the content.
- Accessibility: Digital publications can be designed with accessibility features, making them more inclusive for people with disabilities. Screen readers, text-to-speech software, and other assistive technologies can be used with e-books and online content.
- Self-Publishing: The rise of electronic publishing has made it easier for authors and content creators to self-publish their work. Platforms like Amazon Kindle Direct Publishing (KDP) and Smashwords enable authors to publish and distribute e-books independently.
- Traditional Publishers: Many conventional publishing houses have responded to electronic publishing by providing digital editions of their books and magazines in addition to print editions. This enables them to reach a larger audience while also adapting to changing consumer tastes.
- Open Access: Electronic publication has also aided the expansion of open access publishing models, in which research papers, academic journals, and other scholarly content are made freely available online, frequently with the support of institutions or research funding.
Electronic publication has changed the way content is created, delivered, and consumed in general. It has enabled a broader diversity of viewpoints to be heard, expedited distribution methods, and offered readers new ways to consume and interact with material.