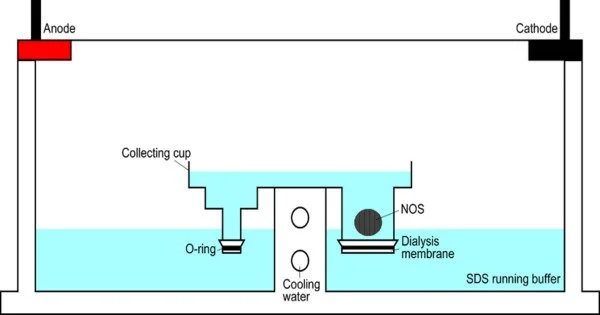
Electroextraction (EE) is a method of extracting chemicals from a solution or matrix by applying an electric field. It is a sample enrichment technique that uses an electric current to focus charged analytes from a vast volume of one phase into a tiny amount of the other phase. It is often used to extract metals from ores and other sources. The process is especially beneficial for recovering metals that are difficult to remove with conventional procedures.
The approach was initially designed as a separation technique for chemical engineering, but it has subsequently been used with capillary electrophoresis and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry to improve detection limits, analysis time, and selectivity. The use of EE-CE has made capillary electrophoresis more applicable to use in the pharmaceutical industry.
Here’s a general overview of the electroextraction process:
- Setup: Electroextraction involves setting up an electrolytic cell, which typically consists of an anode and a cathode immersed in an electrolyte solution. The substance to be extracted is also present in the solution.
- Electric Field Application: When an electric potential is applied across the anode and cathode, an electric field is created within the electrolyte solution.
- Ion Migration: The electric field causes ions in the solution, including the metal ions to be extracted, to migrate towards the electrode of opposite charge. For example, positively charged metal ions move towards the cathode (negatively charged electrode), while negatively charged ions move towards the anode (positively charged electrode).
- Electrochemical Reactions: At the electrodes, electrochemical reactions take place. Reduction reactions occur at the cathode, leading to the deposition of the metal, while oxidation reactions occur at the anode. These reactions play a crucial role in the extraction process.
- Metal Recovery: The metal ions get reduced and deposit onto the cathode as solid metal. This allows for the separation and recovery of the desired metal from the solution.
Applications
Electroextraction is utilized in a variety of industrial processes, including the separation of metals such as copper, zinc, and nickel from their ores. It is frequently preferred when traditional processes, such as smelting, are inefficient or environmentally unfriendly. Furthermore, electroextraction is selective, allowing for the extraction of certain metals from complicated combinations.
The efficiency and feasibility of electroextraction are determined by elements such as the electrolyte’s composition, the electrode material, and the specific qualities of the chemical being extracted. This approach has applications in hydrometallurgy, wastewater treatment, and other sectors that need selective ion extraction.