Disufenton sodium (Cerovive, OKN-007, NXY-059, HPN-07) is a free radical trapping nitrone-based antioxidant compound that has been under development for several medical conditions. It is a nitrone-based compound with potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Initially developed as a neuroprotective agent, it scavenges free radicals and inhibits oxidative stress. It has shown promise in treating conditions like ischemic stroke, traumatic brain injury, and glioblastoma.
Disufenton Sodium works by modulating reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, reducing cell damage, and improving outcomes in preclinical models. It crosses the blood-brain barrier and has demonstrated low toxicity. Research is ongoing to evaluate its effectiveness in cancer therapy, particularly brain tumors, due to its anti-tumor and anti-angiogenic effects.
Chemistry
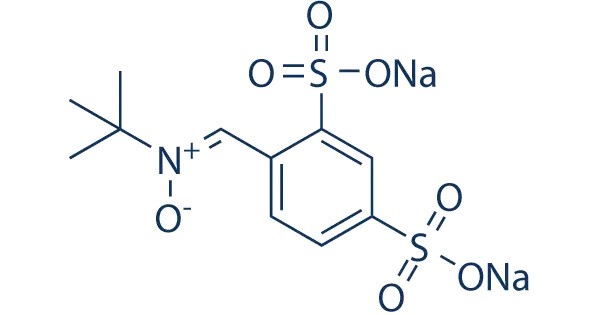
Disufenton sodium is the disulfonyl derivative of the neuroprotective nitrone spin trap phenylbutylnitrone or “PBN”. PBN and its derivatives hydrolyze and oxidize in vitro to form respectively MNP-OH (AKA, NtBHA) and its parent spin-trap MNP.
Properties
- Chemical Name: Disufenton Sodium
- Molecular Formula: C10H12N2Na2O8S2
- Molecular Weight: 402.31 g/mol
- Structure Type: Disulfonated nitrone derivative
- Chemical Class: Nitrone spin trap (a class of antioxidant molecules)
- Water Solubility: Highly soluble due to sodium sulfonate groups
- Appearance: White to off-white crystalline solid
Mechanism of Action
Disufenton Sodium acts as a free radical scavenger, specifically targeting reactive oxygen species (ROS). It is structurally a nitrone, which allows it to “trap” free radicals by forming more stable nitrone-radical adducts.
- Antioxidant Activity: It neutralizes harmful radicals like superoxide and hydroxyl radicals.
- Neuroprotective Role: Initially developed for stroke treatment.
- Anti-tumor Potential: Ongoing research into glioblastoma and other cancers.
Use
Disufenton Sodium is synthetic and does not occur naturally. It has been developed and studied mainly in the context of pharmaceutical research.
- Stroke (Cerebral Ischemia): Originally developed by AstraZeneca under the name NXY-059 for neuroprotection during ischemic stroke. Showed promise in early trials (e.g., SAINT I), but failed in SAINT II, a larger Phase III clinical trial.
- Brain Tumors (e.g., Glioblastoma): The compound was re-investigated as OKN-007 by other research groups, including Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation. Shown to suppress tumor growth in animal models by modulating oxidative stress and inflammatory pathways.
- Other CNS Disorders: Preclinical studies have explored its use in traumatic brain injury, Alzheimer’s disease, and multiple sclerosis.
Research
Disufenton sodium was under development at the drug company AstraZeneca. A 2005 phase-3 clinical trial called “SAINT-1” reported some efficacy in the acute treatment of ischemia injury due to stroke. However, a 2006 attempt to repeat this trial indicated no significant activity. After ruling out other causes, the authors tentatively attributed the positive results in the first trial to “chance”.