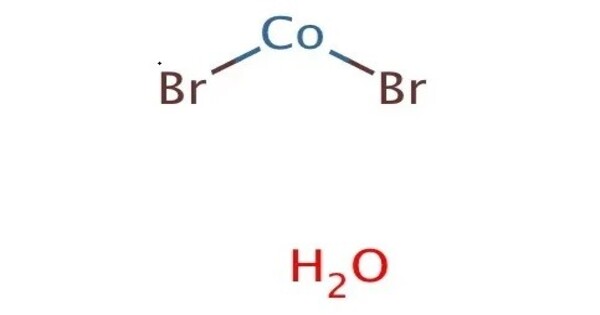
Cobalt(II) bromide (CoBr2) is an inorganic compound. It typically appears as a red or purple solid, depending on its hydration state. In its anhydrous form, it is a green solid that is soluble in water, used primarily as a catalyst in some processes. It is used in various applications, including as a catalyst in chemical reactions, in the preparation of other cobalt compounds, and in some electroplating processes.
It is soluble in water, and its solutions can conduct electricity due to the presence of ions. Cobalt compounds can be hazardous, so proper safety precautions should be taken when handling them, including using gloves and eye protection.
Properties
Cobalt(II) bromide typically appears as a red or reddish-brown crystalline solid. It is soluble in water and alcohol but insoluble in ether. The solubility increases with temperature. It reacts with acids to release bromine and can also undergo oxidation reactions.
- Chemical formula: CoBr2, CoBr2.6H2O, CoBr2.2H2O
- Molar mass: 218.7412 g/mol (anhydrous), 326.74 g/mol (hexahydrate)
- Appearance: Bright green crystals (anhydrous), Red-purple crystals (hexahydrate)
- Density: 4.909 g/cm3 (anhydrous), 2.46 g/cm3 (hexahydrate)
- Melting point: 678 °C (1,252 °F; 951 K) (anhydrous), 47 °C (hexahydrate)
Preparation and reactions
Cobalt(II) bromide can be prepared as a hydrate by the reaction of cobalt hydroxide with hydrobromic acid:
Co(OH)2 + 2HBr → CoBr2·6H2O
The classical coordination compound bromopentaamminecobalt(III) bromide is prepared by oxidation of an aqueous solution of cobalt(II) bromide and ammonia.
2 CoBr2 + 8 NH3 + 2 NH4Br + H2O2 → 2 [Co(NH3)5Br]Br2 + 2 H2O
Triphenylphosphine complexes of cobalt(II) bromide have been used as a catalysts in organic synthesis.
Occurrences
Cobalt(II) bromide is not commonly found in nature in significant quantities. However, cobalt itself is found in minerals such as cobaltite, erythrite, and skutterudite.
Industrial Production
It is typically produced synthetically for use in various applications, including catalysts, pigments, and in the preparation of other cobalt compounds.
Applications
Beyond its chemical uses, cobalt(II) bromide is utilized in research, electronics, and as a reagent in organic synthesis.
Safety
Cobalt compounds can be toxic, and precautions should be taken when handling them, especially in dust or fume form. Exposure to large amounts of cobalt(II) can cause cobalt poisoning. Bromide is also mildly toxic.