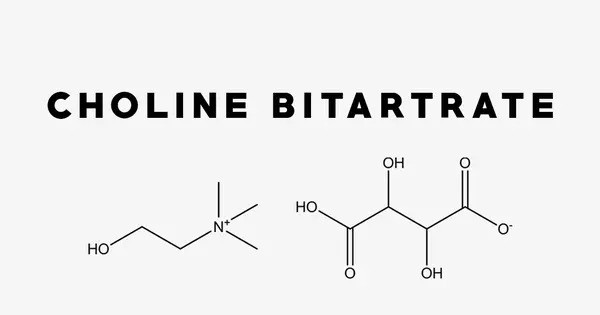
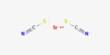
Choline bitartrate is a salt form of choline, an essential nutrient vital for brain health, liver function, and cell membrane formation. It is an organic compound with the chemical formula [(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]+HOOC−CH(OH)−CH(OH)−COO−. It combines choline with tartaric acid, enhancing stability and bioavailability. It is a white crystalline powder with an acid taste. It is hygroscopic when exposed to air.
Choline is a precursor to acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in memory, mood, and muscle control. It also supports lipid metabolism, aiding liver health by preventing fat accumulation. Found in foods like eggs, liver, and soybeans, choline bitartrate is commonly used as a dietary supplement to address deficiencies, particularly in individuals with limited dietary intake, such as vegans or pregnant women. Recommended daily intake varies: 425 mg for women, 550 mg for men, with higher needs during pregnancy (up to 930 mg).
Properties
- Molecular Weight: 253.25 g/mol
- Appearance: White, crystalline powder, often odorless or with a faint trimethylamine-like odor.
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohol, and insoluble in neutral solvents like ether or chloroform.
- Stability: Hygroscopic (absorbs moisture from the air), requiring storage in dry conditions. Stable under normal conditions but may degrade with prolonged exposure to heat or moisture.
- pH: Aqueous solutions are slightly acidic due to the tartaric acid component.
- Function: Acts as a source of choline, an essential nutrient involved in neurotransmitter synthesis (acetylcholine), cell membrane integrity (phospholipids), and lipid metabolism.
Chemistry
Choline bitartrate is a choline salt of tartaric acid. Choline bitartrate contains quaternary ammonium cations ((2-hydroxyethyl)trimethylammonium [(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]+) and bitartrate anions (HOOC−CH(OH)−CH(OH)−COO−). Quaternary ammonium cation is a cation in which all four hydrogen atoms of ammonium are replaced with organyl groups. In the choline cation, the four substituents of ammonium are three methyl groups (−CH3) and one 2-hydroxyethyl group (−CH2CH2OH). The bitartrate anion is chiral (there are left, right and meso forms of bitartrate, see tartaric acid).
Production
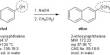
Choline bitartrate can be produced by the chemical reaction of trimethylamine with ethylene oxide and water, followed by reaction with tartaric acid.
N(CH3)3 + CH2CH2O + H2O → [(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]+OH− [(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]+OH− + C4H6O6 → [(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]+C4H5O−6 + H2O
Occurrences
Choline bitartrate does not occur naturally in significant amounts in foods or the environment. Instead, it is synthetically produced for use as a dietary supplement and food additive. However, choline itself is naturally present in various foods, and choline bitartrate is derived from these natural choline sources combined with tartaric acid. Key points about its occurrence and use:
- Synthetic Production: Choline bitartrate is manufactured by combining choline (often derived from natural sources like lecithin in soybeans or egg yolks) with tartaric acid, a naturally occurring organic acid found in grapes and other fruits.
- Dietary Supplements: Widely used in supplements to provide choline, supporting cognitive function, liver health, and fat metabolism. It’s often found in nootropic stacks, prenatal vitamins, and general health supplements.
- Food Additives: Used in some fortified foods and beverages to boost choline content, though less common than other choline forms like lecithin.
- Natural Choline Sources: While choline bitartrate itself is synthetic, choline is naturally abundant in foods like egg yolks, liver, soybeans, beef, chicken, fish, and cruciferous vegetables (e.g., broccoli, cauliflower). These foods contain choline in forms like phosphatidylcholine, glycerophosphocholine, or free choline, not as bitartrate.
- Pharmaceutical and Industrial Uses: Choline bitartrate is used in some pharmaceutical formulations and as a precursor in the synthesis of other choline-based compounds.
Uses
Choline bitartrate is used as a dietary supplement, a food additive, a nutrient and as a lipotropic compound. It is also used as a medication against bipolar disorder and mania. Certain conducted double-blind, placebo-controlled studies of the effects of choline bitartrate treatment against Alzheimer-type dementias suggest improvement in some areas of patients’ cognitive performance.
Supplements typically provide 250–1000 mg per dose, with 40% choline by weight. Benefits include improved cognitive function, reduced risk of neural tube defects in pregnancy, and potential liver protection. However, excessive intake (>3.5 g/day) may cause side effects like nausea, sweating, or a fishy odor.
Safety
Choline bitartrate is flammable. When burned, choline bitartrate may release toxic gases, like carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2) and nitrogen oxides (NO, NO2). May react violently with strong oxidizing agents.