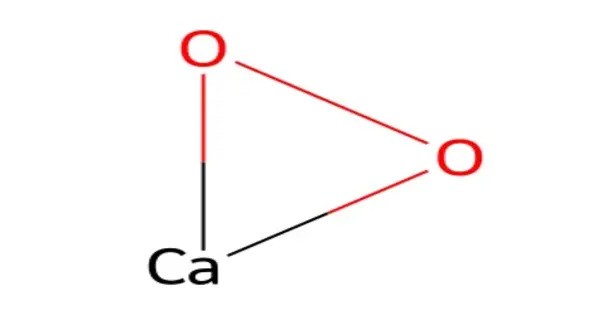
Calcium peroxide or calcium dioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula CaO2. It is the peroxide (O22−) salt of Ca2+. Commercial samples can be yellowish, but the pure compound is white. It is almost insoluble in water. It’s commonly used as an oxidizing agent and has a variety of applications, including in water treatment, soil remediation, and as a component in certain bleaching processes.
Properties
It typically appears as a white powder or granules. It is slightly soluble in water, where it can release oxygen and form calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂). It reacts with acids to release oxygen and can be used as a disinfectant or to treat water for oxygenation.
- Chemical formula: CaO2
- Molar mass: 72.076 g·mol−1
- Appearance: white or yellowish powder
- Odor: odorless
- Density: 2.91 g/cm3
- Melting point: ~ 355 °C (671 °F; 628 K) (decomposes)
- Solubility in water: decomposes
- Acidity (pKa): 12.5
- Crystal structure: Orthorhombic
Structure and stability
As a solid, it is relatively stable against decomposition. In contact with water however it hydrolyzes with release of oxygen. Upon treatment with an acid, it forms hydrogen peroxide.
Preparation
Calcium peroxide is produced by combining calcium salts and hydrogen peroxide:
Ca(OH)2 + H2O2 → CaO2 + 2 H2O
The octahydrate precipitates upon the reaction of calcium hydroxide with dilute hydrogen peroxide. Upon heating it dehydrates.
Occurrences
- Natural Sources: Calcium peroxide is found in trace amounts in some minerals. It may also form in certain geochemical conditions, such as in soils or rocks with sufficient calcium and oxygen.
- Biological Relevance: While not commonly found in biological systems, calcium peroxide can be used in some controlled biological settings to introduce oxygen in hypoxic conditions.
Applications
It is mainly used as an oxidant to enhance the extraction of precious metals from their ores. In its second main application, it is used as a food additive under the E number E930 it is used as flour bleaching agent and improving agent.
One of its most notable uses is in the remediation of contaminated water or soil. When calcium peroxide decomposes, it releases oxygen over time, which can help break down organic pollutants or improve the aerobic conditions needed for biodegradation processes. It’s also used in some agricultural practices, such as improving soil aeration or as a fertilizer additive.
In agriculture it is used in the presowing treatments of rice seed. Also, it has found use in aquaculture to oxygenate and disinfect water. In the ecological restoration industry it is used in the treatment of soils.