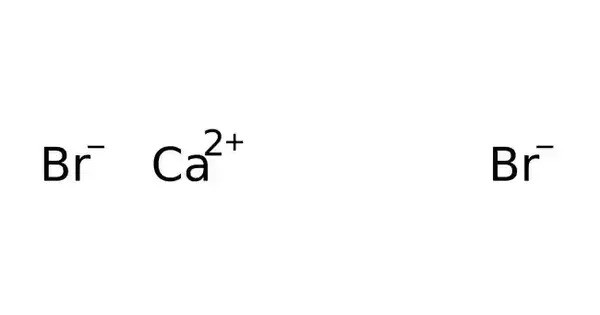
Calcium bromide is the name for compounds with the chemical formula CaBr2(H2O)x. Individual compounds include the anhydrous material (x = 0), the hexahydrate (x = 6), and the rare dihydrate (x = 2). It typically appears as a white crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water. All are white powders that dissolve in water, and from these solutions crystallizes the hexahydrate. The hydrated form is mainly used in some drilling fluids.
It is a useful and versatile compound, primarily in industrial applications such as drilling fluids, water treatment, and chemical manufacturing. While it can occur naturally in certain brines and salt deposits, most commercial calcium bromide is synthetically produced. Its key properties include high solubility in water, hygroscopicity, and use in enhancing the density of drilling fluids.
Properties
- Chemical formula: CaBr2
- Molar mass: 199.89 g/mol (anhydrous), 235.98 g/mol (dihydrate)
- Appearance: anhydrous is hygroscopic colorless crystals, sharp saline taste
- Density: 3.353 g/cm3
- Melting point: 730 °C (1,350 °F; 1,000 K)
- Boiling point: 1,815 °C (3,299 °F; 2,088 K) (anhydrous), 810 °C (dihydrate)
- Solubility in water: 125 g/100 mL (0 °C), 312 g/100 mL (100 °C)
- Solubility in alcohol, acetone: soluble
Chemical Properties
Reactivity: Reacts with strong acids like sulfuric acid to release hydrogen bromide (HBr) gas.
Decomposition: When heated strongly, it can decompose to form calcium oxide (CaO) and bromine gas (Br₂).
Solubility in Water: When dissolved in water, calcium bromide forms a highly concentrated, ionic solution. The solution is used in various applications, such as in the oil industry and in laboratory experiments.
Synthesis, structure, and reactions
It is produced by the reaction of calcium oxide, calcium carbonate with bromine in the presence of a reducing agent such as formic acid or formaldehyde:
CaO + Br2 + HCO2H → CaBr2 + H2O + CO2
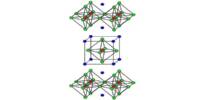
Solid calcium bromide adopts the rutile structure, featuring octahedral Ca2+ centres bound to six bromide anions, which also bridge to other Ca2+ centres.
When strongly heated in air, calcium bromide reacts with oxygen to produce calcium oxide and bromine:
2 CaBr2 + O2 → 2 CaO + 2 Br2
Occurrences
Natural Sources: Bromine-containing Salts: Calcium bromide is not as common in nature as other calcium salts (like calcium carbonate), but it can be found in certain brine solutions, particularly in seawater and salt lakes where bromine salts are dissolved.
Brine Wells and Salt Deposits: It can also be found in natural brines, either in its pure form or as part of a mixture of salts in mineral deposits.
Coastal Areas: Calcium bromide, along with other bromides, can be found in seawater, especially in the Mediterranean, the Dead Sea, and other salt-rich bodies of water.
Uses
It is mainly used as dense aqueous solutions for drilling fluids. It is also used in neuroses medication, freezing mixtures, food preservatives, photography and fire retardants.
- Drilling Fluids: It is used in the oil and gas industry as part of drilling fluids.
- Dyeing and Photography: It can be used in certain photographic processes and dyeing.
- Fire Extinguishing: It can serve as a component in some fire extinguishing systems.
- Heat Transfer Fluids: It is used in some applications for heat transfer due to its high solubility and low freezing point.