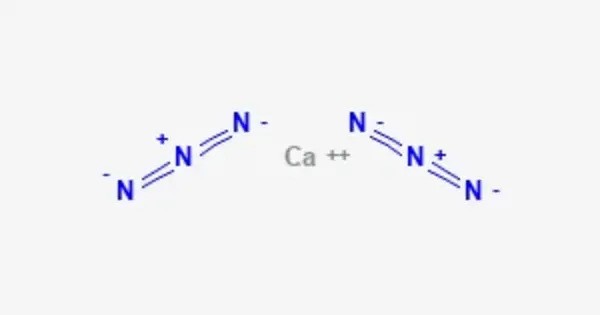
Calcium azide is a chemical compound with the formula Ca(N3)2. It is sparingly soluble in water, which limits its applications in some contexts. It is relatively stable under normal conditions but can decompose upon heating or in the presence of strong acids, releasing nitrogen gas (N2). It has a decomposition temperature that leads to the release of nitrogen and other compounds, making it a subject of study for energetic materials.
Properties
It is typically a white or colorless solid. It is generally soluble in water, dissociating into calcium and azide ions. It can be sensitive to heat and shock, making it potentially hazardous. Azides, in general, are known for their explosive properties.
- Chemical formula: Ca(N3)2
- Molar mass: 124.12 g/mol
- Appearance: colorless crystals
- Melting point: 100 °C (212 °F; 373 K) decomposes at 150 °C
- Solubility in water: 38.1 g/100 mL (0 °C)
- Solubility: slightly soluble in ethanol, insoluble in ether, acetone
Production
Calcium azide is not commonly found in nature but can be synthesized in laboratories or industrial settings for various applications. It can be obtained from a distilled reaction between hydrazoic acid and calcium hydroxide.
Reactivity
Calcium azide is sensitive to shock and can be explosive, especially in finely divided forms. This makes handling and storage critical.
Uses in Industry
It is primarily used in the production of explosives and pyrotechnics, due to its energetic properties.
Safety
Calcium azide is sensitive to impact, in which it may detonate and ignite. Due to the potential hazards associated with azides, including toxicity and explosive properties, handling calcium azide requires proper safety precautions.