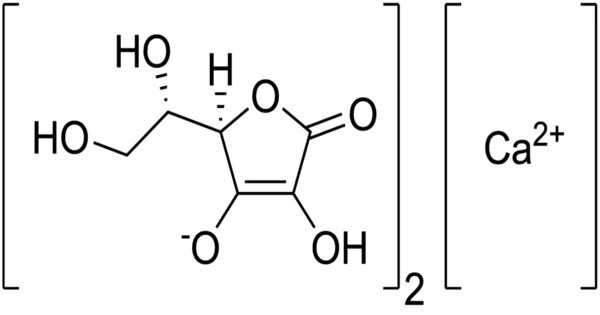
Calcium ascorbate is a compound with the molecular formula CaC12H14O12. It is the calcium salt of ascorbic acid, one of the mineral ascorbates. It is approximately 10% calcium by mass. It’s commonly used as a dietary supplement to provide both vitamin C and calcium. It helps in collagen formation, boosts immune function, and has antioxidant properties. It is generally well-absorbed in the body and can be a good option for individuals who need both calcium and vitamin C in their diets.
Calcium ascorbate is known to be less acidic than regular ascorbic acid, making it gentler on the stomach. As a food additive, it has the E number E 302. It is approved for use as a food in the EU, USA and Australia and New Zealand.
Properties
- Chemical formula: Ca(C6H7O6)2
- Molar mass: 390.310 g·mol−1
- Solubility in water: About 50 g/100 mL
- Solubility: Slightly soluble in alcohol; insoluble in ether
Natural Occurrence
Calcium ascorbate does not naturally occur in foods in its pure form, but ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is widely found in fruits and vegetables, particularly citrus fruits (oranges, lemons), strawberries, and bell peppers. To form calcium ascorbate, calcium salts are added to ascorbic acid, which can be achieved through industrial processes.
Production
Calcium ascorbate is synthesized by reacting calcium carbonate or calcium hydroxide with ascorbic acid. This results in the formation of calcium ascorbate and water, making it a commonly produced compound in the pharmaceutical and food industries.
Use in Supplements and Fortified Foods:
It is commonly found in dietary supplements, particularly in those designed for individuals who need vitamin C but also require a non-acidic form of it (e.g., for people with gastrointestinal sensitivity). Calcium ascorbate is often included in multivitamins, effervescent tablets, and chewable vitamin C supplements.
Food Additive
As a food additive, calcium ascorbate is used to preserve the freshness of products, particularly in fruit juices and processed foods. It can also be used to prevent discoloration and improve the stability of vitamin C in processed foods.
Health Benefits
Calcium ascorbate, like ascorbic acid, plays a crucial role in:
- Immune function: Boosting immune system activity.
- Collagen synthesis: Important for the health of skin, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, and blood vessels.
- Antioxidant protection: Protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals.
- Bone health: Due to its calcium content, it also supports bone strength and density.