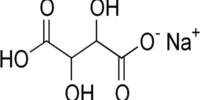
Cadmium permanganate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Cd(MnO4)2. It can form the hexahydrate Cd(MnO4)2·6H2O. It is an inorganic permanganate salt that commonly occurs as dark purple crystals and as a hexahydrate (Cd(MnO₄)₂·6H₂O). It is water-soluble and a powerful oxidizing agent (permanganate/ Mn⁷⁺ chemistry).
Like other cadmium compounds, it is toxic and poses health and environmental hazards, particularly due to cadmium’s carcinogenic nature and manganese’s oxidative reactivity. Its melting point is not well defined because it decomposes before reaching a liquid state.
Preparation
Cadmium permanganate can be obtained by reacting cadmium sulfate and barium permanganate. After removing the barium sulfate precipitate, the solution is crystallized in the dark:
Ba(MnO4)2 + CdSO4 → Cd(MnO4)2 + BaSO4↓
Cadmium permanganate can also be produced by reacting manganese heptoxide with cadmium oxide or cadmium hydroxide.
Properties
Cadmium permanganate hexahydrate loses water of crystallisation at 61~62 °C, and anhydrate can be obtained at a constant temperature of 90 °C. The anhydrous form begins to decompose at 108 °C: Cd(MnO4)2 → CdMnO3 + MnO2 + 3/2 O2↑
- Chemical formula: Cd(MnO4)2
- Molar mass: 350.28
- Appearance: dark purple crystals
- Solubility in water: soluble
It appears as a dark, crystalline solid with strong oxidizing properties due to the permanganate ion. The compound is unstable at high temperatures and can decompose, releasing oxygen and manganese oxides. It is highly soluble in water, forming intensely purple-colored solutions typical of permanganates.
Synthesis
Prepared by metathesis (e.g., cadmium sulfate + barium permanganate, remove BaSO₄) or by treating cadmium oxide/hydroxide with strong permanganating reagents; the hexahydrate loses water near 61–62 °C and the anhydrous salt begins to decompose above ≈108 °C.
Occurrences
Cadmium permanganate does not occur naturally in the Earth’s crust. It is a synthetic compound, prepared in laboratories by reacting a soluble cadmium salt (such as cadmium nitrate or cadmium sulfate) with a permanganate salt (like potassium permanganate). Its occurrence is limited to chemical research and specialized applications, as its toxicity and instability prevent widespread industrial or commercial use. It is primarily studied for its oxidizing strength and coordination chemistry rather than for practical large-scale applications.
Hazards & handling
It combines two serious risks — cadmium toxicity (systemic poison, carcinogen; strict exposure limits) and strong oxidative reactivity (can ignite/accelerate combustion of organics). Store in a cool, dry, ventilated area away from combustibles and reducing agents; use appropriate PPE and follow local hazardous-waste disposal rules. In case of spills, avoid organic absorbents and consult an MSDS or institutional safety office.