The chemical formula for ammonium paratungstate (or APT) is (NH4)10(H2W12O42)•4H2O. It’s been called “the most crucial raw material for all other tungsten products.” When heated to between 220 and 280 degrees Celsius, ammonium paratungstate loses some of its ammonium and water components and transforms into ammonium metatungstate.
It is insoluble in water and is mostly used to make ammonium metatungstate, tungsten oxide, and tungsten powder. Heating ammonium paratungstate to 220-280°C results in the loss of some ammonia and crystal water, which can be transformed into ammonium metatungstate AMT; heating above 600°C results in the loss of all ammonia and crystal water and complete transformation into tungsten trioxide.
Properties
Ammonium paratungstate (or APT) is a white crystalline ammonium-tungsten salt. It has the shape of a sheet or a needle. It is water and alcohol insoluble. Ammonium metatungstate is a versatile raw material that can be used to make catalysts, capacitors, nuclear shielding, flame retardants, corrosion inhibitors, ultra-fine tungsten powder, tungsten heavy alloy powder, phosphotungstic acid, arsenic acid, and silicon tungstate.
- Molecular Weight: 3042.44 (anhydrous)
- Appearance: White crystalline powder
- Melting Point: >300°C
- Boiling Point: 600°C (dec.)
- Density: 2.3 g/cm3
- Solubility in H2O: N/A
- Exact Mass: 3041.547116

Production
- From tungsten ores
Tungsten ores, which are typically oxides, are digested in the base to give solutions of tungstate together with many contaminating species. This crude extract is acidified and treated with sulfide to separate molybdenum trisulfide. Upon further acidification, APT eventually crystallizes.
- Laboratory methods
If a calcined WO3 is used, refluxing the ammonia solution is advisable to accelerate its dissolution.
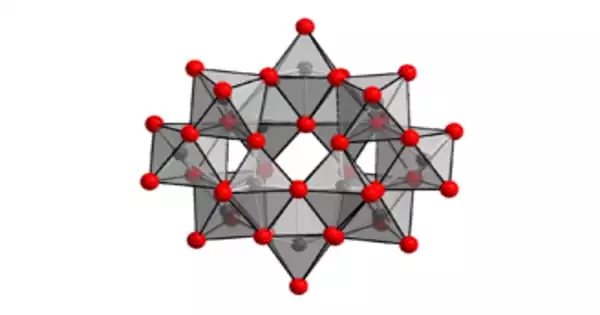
Structure
The anion in (NH4)10(W12O41)•5H2O has been proven to be [H2W12O42]10−, with two hydrogen atoms inside the cage. Ammonium paratungstate’s correct formula notation is (NH4)10[H2W12O42]•4H2O. The paratungstate B ion is known as [H2W12O42]10−, as opposed to the paratungstate A ion, which has the formula [W7O24]6−, comparable to the paramolybdate ion. However, NMR spectroscopy could not prove the existence of the paratungstate an ion.
Before about 1930, there has been some dispute about the exact composition of the salt, and both (NH4)10W12O41 and (NH4)6W7O24 were proposed. O.W. Gibbs remarked about this:
“The alkali tungstates are numerous and unusually complex. Salts of essentially different formulae approach so closely in percentage composition, that the differences lie very near the unavoidable errors of analyses. The analyses are hardly sufficiently close to decide the question upon purely analytical grounds.”
Applications
It is a chemical compound that consists primarily of white crystals with two shapes: sheet-like or needle-like, and is used in the production of tungsten trioxide or tungsten blue oxide powder. Ammonium metatungstate and other tungsten compounds are also produced as petrochemical additives.
Mainly used in the production of tungsten metal powder such as tungsten trioxide or tungsten blue oxide; downstream products of metallic tungsten powder include tungsten material series such as tungsten, tungsten and other electric vacuum materials; alloy series such as tungsten carbide alloy blade, alloy drill, alloy molds, etc.; and other wear, pressure, temperature, and other machinery and equipment components.