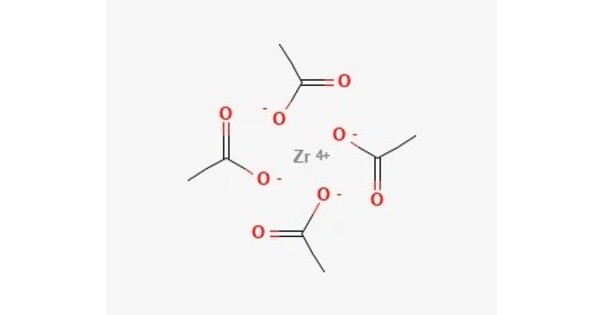
Zirconyl acetate is the coordination complex with the formula Zr6O4(OH)4(O2CCH3)12. It is a chemical compound that consists of zirconium, oxygen, and acetate ions. It is a white solid prepared by treating zirconyl chloride with acetic acid. The compound has attracted attention as a precursor to metal-organic frameworks. The structure of the 8.5 hydrate has been determined by EXAFS. The core can be described as a Zr6 octahedron is face-capped with oxide and hydroxide ligands. It is typically used in various industrial applications, including as a catalyst in organic synthesis and as a precursor for other zirconium compounds.
Physical Properties
- Appearance: Usually appears as a white crystalline solid or powder.
- Solubility: Soluble in water, forming acidic solutions.
- Melting Point: Decomposes upon heating, rather than melting cleanly.
- Density: Varies depending on the form (solid or solution).
- Molecular Weight: Approximately 259.38 g/mol
Chemical Properties
- Stability: It is relatively stable under normal conditions but decomposes when heated to form zirconium dioxide (ZrO2).
- pH: Aqueous solutions of zirconyl acetate are acidic.
- Reactivity: It reacts with bases to form zirconium hydroxide and with acids to form zirconium salts.
Applications
- Catalysis: Used as a catalyst in various chemical reactions.
- Textiles: Employed in the textile industry for improving the dyeing process.
- Coatings: Utilized in the preparation of coatings and finishes.
- Ceramics: Acts as a precursor for the preparation of zirconium-based ceramics.
Handling and Safety
- Safety Measures: Proper protective equipment such as gloves and goggles should be worn to avoid contact with skin and eyes.
- Hazards: Can cause irritation to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract.