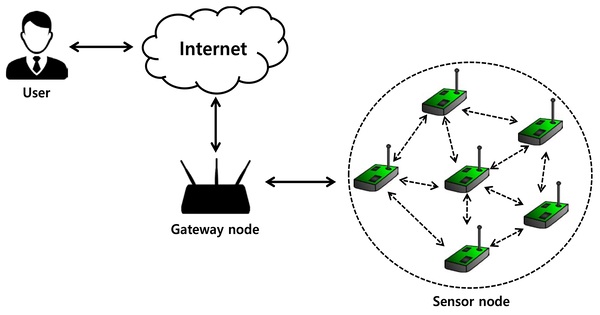
A wireless sensor network (WSN) is a network of devices that use wireless connectivity to communicate information gathered from a monitored field. The data is routed across many nodes and connects to other networks such as wireless Ethernet via a gateway. End sensor nodes, routing nodes, and base station or data collection sink nodes comprise a WSN (or base station or gateway). To provide an efficient and dependable network, the WSN should be scalable and secure.
WSNs are categorized according to network type, clustering, communication mechanism, protocol, application utilization, and coverage. WSNs are networks of autonomous sensing devices that are spatially distributed and used to monitor physical or environmental conditions such as temperature, pressure, sound, vibration, motion, or pollution at various locations. In a WSN, all nodes connect wirelessly and use different routing methods. WSNs work in environments with limited bandwidth and performance. WSNs are multi-hop ad hoc networks that self-organize.
These networks are utilized in environmental tracking applications such as forest identification, animal tracking, flood detection, forecasting, and weather prediction, as well as commercial applications such as seismic activity prediction and monitoring.
Benefits or advantages of WSN –
Following are the benefits or advantages of WSN:
- Because it is scalable, it can accommodate any new nodes or devices at any moment.
- It is adaptable and so open to physical partitioning.
- A centralized monitoring system allows access to all WSN nodes.
- Because it is wireless, it does not require wires or cords. Refer to the distinction between a wired network and a wireless network.
- WSNs can be used on a big scale and in a variety of areas such as mines, healthcare, surveillance, agriculture, and so on.
- It employs several security methods in accordance with the underlying wireless technology, resulting in a dependable network for consumers or users.
Drawbacks or disadvantages of WSN
Following are the drawbacks or disadvantages of WSN:
- Because it is wireless, it is vulnerable to hacking.
- Because it is designed for low-speed applications, it cannot be utilized for high-speed communication.
- Building such a network is expensive, and thus not affordable to everyone.
- Energy efficiency, restricted bandwidth, node costs, deployment model, software/hardware design constraints, and so on are all factors to consider in WSN.
- In a WSN with a star topology, the failure of the central node causes the entire network to shut down.
The limitations of wireless sensor networks include the following.
- Possess very little storage capacity – a few hundred kilobytes
- Possess modest processing power-8MHz
- Works in short communication range – consumes a lot of power
- Requires minimal energy – constrains protocols
- Have batteries with a finite lifetime
- Passive devices provide little energy
WSN employs several topologies such as star, tree, mesh, hybrid, and so on. As a result, one may comprehend the pros and cons of different topologies to infer the benefits and drawbacks of WSN. Furthermore, WSN employs a variety of underlying wireless technologies. As a result, one can discuss the benefits and drawbacks of Zigbee, Z-wave, WiFi, and WiFi6, among other technologies.