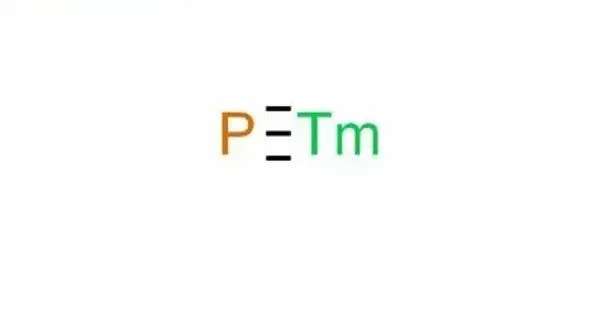Thulium phosphide is an inorganic compound of thulium and phosphorus with the chemical formula TmP. It is part of the group of rare-earth phosphides, which typically feature elements from the lanthanide series, and it shares many properties with other lanthanide phosphides. It is usually a solid, and its appearance can range from dark metallic gray to black, depending on its form and purity.
Structure
Thulium phosphide typically forms a crystalline structure, similar to other rare-earth phosphides. The crystal lattice often exhibits a rock salt structure (NaCl-type), though variations can occur depending on the exact conditions of synthesis.
Properties
Thulium phosphide is a semiconductor and can exhibit interesting electronic and optical properties, such as unique magnetic and electrical behaviors. It also has applications in various high-tech fields, though its specific use cases may be more specialized compared to other, more widely used materials.
- Chemical formula: PTm
- Molar mass: 199.90
- Appearance: Crystals
- Density: 7.62 g/cm3
The dense phosphide film will prevent further reactions inside the metal. After etching gallium arsenide, an epitaxial layer of thulium phosphide can be grown on the surface to obtain a TmP/GaAs heterostructure. The compound forms crystals of a cubic system, space group Fm3m. TmP crystallizes in a NaCl-type structure at ambient pressure.
Synthesis
Reaction of thulium metal with phosphorus:
4 Tm + P4 → 4 TmP
Uses
The compound is a semiconductor used in high power, high frequency applications and in laser and other photo diodes.
- Optical and Photonic Applications: Due to thulium’s use in laser technologies (especially in the mid-infrared range), thulium phosphide might have potential in optoelectronic devices, such as laser diodes, phosphorescent coatings, or as a component in optical communication systems.
- Semiconductors: As a semiconductor, thulium phosphide could have applications in electronics, particularly in niche or specialized devices, like high-temperature or high-radiation environments.
- Materials Science: Phosphides of rare-earth elements like thulium are of interest in materials science for their potential magnetic and electronic properties, which might be useful in new materials for energy storage, sensors, or advanced electronic devices.