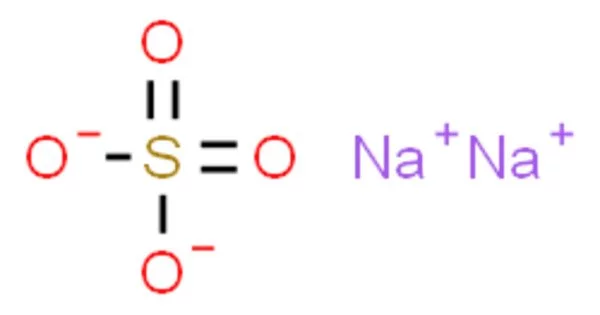Sodium sulfate (also known as sodium sulphate or soda sulfate) is an inorganic compound with the formula Na2SO4 and a number of related hydrates. All forms are white solids that are extremely water soluble. The decahydrate is a major commodity chemical product, with an annual production of 6 million tonnes. It is primarily used as a filler in the production of powdered home laundry detergents as well as in the Kraft process of paper pulping for the production of highly alkaline sulfides.
It is a white crystalline solid that is water soluble and is widely used in a wide range of industrial applications. One of the most common applications for sodium sulfate is as a filler in detergents, where it increases the bulk of the product while also improving its cleaning properties. It’s also used as a desiccant to absorb moisture in a variety of products, including drywall and cement.
Properties
- Melting and boiling point: It has a melting point of 884°C (1,623°F) and a boiling point of 1,429°C (2,604°F).
- Density: The density is 2.664 g/cm3.
- Solubility: It is highly soluble in water, with a solubility of 48.6 g/100 mL at 20°C. It is also soluble in glycerol and slightly soluble in ethanol.
- pH: A 1% solution of sodium sulfate has a pH of 7, which is neutral.
- Hygroscopicity: It is hygroscopic, meaning it can absorb moisture from the air.
Production
Sodium sulfate is stable under normal conditions, but it can react with strong acids to produce sulfuric acid and with strong oxidizing agents to produce sodium sulfite or sodium sulfide.
The global production of sodium sulfate, almost entirely in the form of decahydrate, is estimated to be between 5.5 and 6 million tonnes per year (Mt/a). In 1985, production was 4.5 Mt/a, with natural sources accounting for half of the total and chemical production accounting for the other half. After 2000, natural production increased to 4 Mt/a, while chemical production decreased to 1.5 to 2 Mt/a, for a total of 5.5 to 6 Mt/a. Natural and synthetic sodium sulfate are practically interchangeable for all applications.
Safety
Although sodium sulfate is generally considered non-toxic, it must be handled with caution. The dust can cause temporary asthma or eye irritation; use eye protection and a paper mask to avoid this risk. There is no restriction on transportation, and no Risk Phrase or Safety Phrase applies.
While sodium sulfate is generally considered to be safe for use in its various applications, it can be harmful if ingested or inhaled in large amounts. It is important to follow proper safety precautions when handling the compound, including wearing protective equipment such as gloves and a respirator when necessary.
Application
Sodium sulfate is used in a variety of applications, including as a filler in detergents, as a component in glass production, in the textile industry as a leveling agent, and as a laxative. It is also used in the manufacture of paper and in the production of certain chemicals.
Sodium sulfate is also used in the production of textiles, paper, and glass, as well as sodium sulfide for use in the pulp and paper industry. In some countries, it can also be used as a food additive under the E number E514.