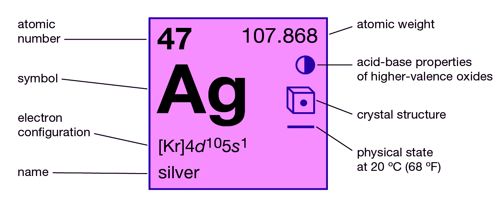
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag and atomic number 47. It is a chemical element, a white lustrous metal valued for its decorative beauty and electrical conductivity. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. It is widely distributed in nature, but the total amount is quite small when compared with other metals; the metal constitutes 0.05 part per million of Earth’s crust.
Silver is a naturally occurring element. It is found in the environment combined with other elements such as sulfide, chloride, and nitrate.
Properties
It tarnishes slowly in the air as sulfur compounds react with the surface forming black silver sulfide.
- atomic number: 47
- atomic weight: 107.868
- melting point: 960.8°C (1,861.4°F)
- boiling point: 2,212°C (4,014°F)
- specific gravity: 10.5 (20°C [68°F])
- oxidation states: +1, +2, +3
Silver can be obtained from pure deposits as well as from silver ores such as horn silver and argentite. It has long been valued as a precious metal. It can also be obtained as a by-product along with deposits of ores containing gold, copper, or lead. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal.
Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as “0.940 fine”. Silver has two other unique properties. It conducts heat and electricity better than any other element. It also reflects light very well. As one of the seven metals of antiquity, silver has had an enduring role in most human cultures.
Occurrences
Silver is a fairly rare element in the Earth’s crust. The metal is found in the Earth’s crust in the pure, free elemental form (“native silver”), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Its abundance is estimated to be about 0.1 parts per million. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc refining.
Uses
Silver is used to making jewelry, silverware, electronic equipment, and dental fillings. It is used to make mirrors, as it is the best reflector of visible light known, although it does tarnish with time. It is also used to make photographs, in brazing alloys and solders, to disinfect drinking water and water in swimming pools, and as an antibacterial agent. It has the highest electrical conductivity of all metals, but it is not widely used for electrical purposes as it is very expensive. Silver paints are used in the manufacture of electronic printed circuits.
Information Source: