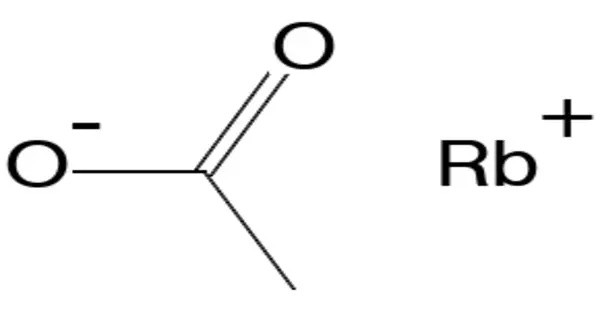
Rubidium acetate is a rubidium salt that is the result of reacting rubidium metal, rubidium carbonate, or rubidium hydroxide with acetic acid. It is soluble in water like other acetates. It appears as a white crystalline solid and is soluble in water. It is typically used in laboratory settings, particularly in research and experiments related to rubidium compounds and their reactions. Rubidium itself is an alkali metal, and rubidium salts like rubidium acetate are often used in scientific applications that involve the study of chemical reactions, ion exchange, and other areas of inorganic chemistry.
Properties
- Molar mass: 144.51 g/mol
- Appearance: White solid
- Melting point: 246 °C (475 °F; 519 K) (decomposes)
- Solubility in water: 85 g/100 ml (45 °C)
- log P: -0.561
Chemical Properties
- Basicity: Rubidium acetate behaves as a basic salt in water, dissociating to release rubidium ions (Rb⁺) and acetate ions (C₂H₃O₂⁻).
- Reaction with acids: It can react with acids to form acetic acid and a rubidium salt, similar to other metal acetates.
- Reaction with bases: It is relatively stable and does not readily react with bases due to the nature of the acetate group.
Occurrences
Rubidium acetate is not commonly found in nature as a pure compound, but rubidium is typically extracted from mineral sources. Rubidium occurs in trace amounts in various minerals, and rubidium salts can be obtained by processing these minerals. Some of the minerals containing rubidium include:
- Leucite
- Pollucite
- Zinnwaldite
Rubidium acetate can be synthesized in laboratories from rubidium salts or by reacting rubidium hydroxide (RbOH) with acetic acid (CH₃COOH) to form the acetate salt.
Rubidium compounds, including rubidium acetate, are often of interest for specialized scientific research, such as studies related to atomic physics, as rubidium atoms are used in certain types of atomic clocks and quantum experiments.
Uses
Rubidium acetate is used as a catalyst for the polymerization of silanol terminated siloxane oligomers. It is primarily used in the laboratory as a reagent, especially in the preparation of rubidium compounds and as a source of rubidium ions. It is also utilized in some analytical chemistry and materials science applications, including studies of rubidium’s role in various chemical systems.