Rhodium pentafluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula Rh4F20. It is a red solid. It is prepared by fluorination of rhodium trifluoride at 400°C. Rhodium is the rarest of all non-radioactive metals. It is considered the rarest and most valuable precious metal in the world — far more so than gold or platinum.
It has a melting point of 1,966°C (3,571°F) and a boiling point of about 4,500°C (8,100°F). Its density is 12.41 grams per cubic centimeter. Two of the metal’s special properties are its high electrical and heat conductivity. Molar Mass: 197.897516 g.
Rhodium pentafluoride is an inorganic compound. It is prepared by fluorination of rhodium trifluoride at 400°C. It occurs uncombined in nature, along with other platinum metals, in river sands in North and South America.
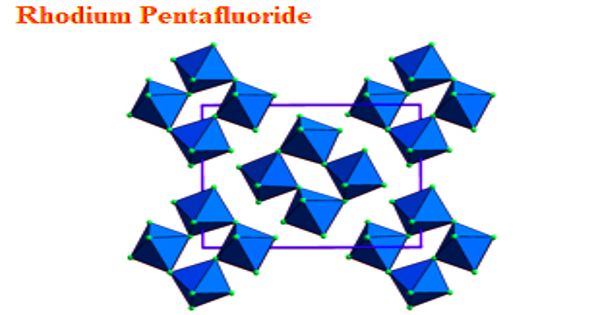
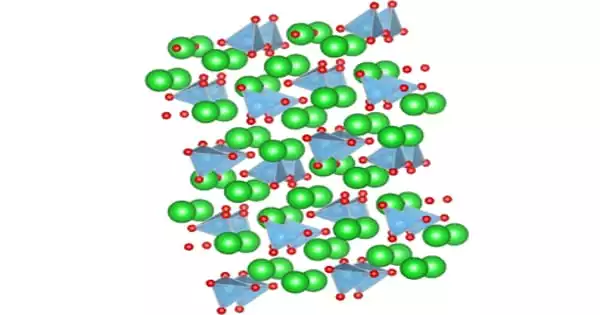
According to X-ray crystallography, the Rh centers are octahedral. The structure is very similar to that of the related ruthenium pentafluoride, osmium pentafluoride, and iridium pentafluoride. All are tetrameric, meaning that they have the molecular structure [MF5]4.
The M-F distances for the bridging fluoride ligands are typically about 0.2 Å longer than the Rh-F distances for the nonbridging fluoride ligands. In the case of rhodium pentafluoride, these distances average 1.999(4) and 1.808(8) Å. The Rh-F-Rh angles average 135°, which leads to a ruffled structure. In contrast, the M-F-M centers are linear in the pentafluorides of niobium, tantalum, molybdenum, and tungsten.
It occurs uncombined in nature, along with other platinum metals, in river sands in North and South America. It is also found in the copper-nickel sulfide ores of Ontario, Canada. Rhodium is obtained commercially as a by-product of copper and nickel refining.
Rhodium compounds are encountered relatively rarely by most people. There are almost no reported cases of a human being affected by this element in any way. All rhodium compounds should be regarded as highly toxic and carcinogenic. Compounds of rhodium stain the skin very strongly.