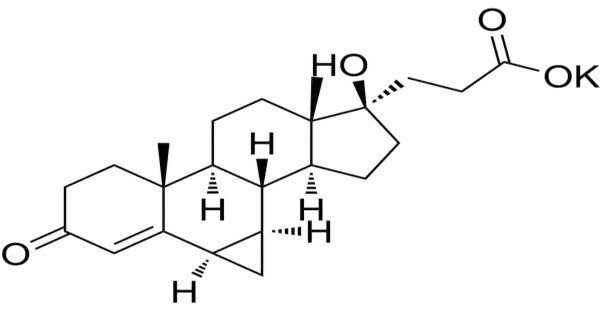
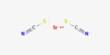
Prorenoate potassium (developmental code name SC-23992) is a synthetic steroidal antimineralocorticoid which was never marketed. It is a potassium salt form of prorenoic acid, a synthetic steroidal antimineralocorticoid. It is structurally related to spironolactone and functions primarily by antagonizing the mineralocorticoid receptor, thereby inhibiting the action of aldosterone. This leads to increased sodium excretion and potassium retention, making it useful in conditions like hypertension, heart failure, and hyperaldosteronism.
Despite its pharmacological potential, prorenoate potassium was never marketed, likely due to limited efficacy, safety concerns, or the availability of more effective alternatives. It has been studied experimentally and used in research to better understand aldosterone’s role in fluid balance and blood pressure regulation.
Properties
- Molecular Formula: C₂₄H₃₁KO₅
- Molar Mass: ~438.6 g/mol
- Chemical Structure: Steroidal backbone, Potassium carboxylate group
- Physical State: Solid (typically a white to off-white powder)
- Solubility: Likely soluble in water due to the potassium salt form; solubility in organic solvents varies depending on pH
Structure
The compound is classified under spirolactones, sharing a core structural feature with spironolactone, and exhibits antiandrogenic properties in addition to its antimineralocorticoid activity. However, its clinical significance remains minimal due to its discontinued development.
Pharmacological Properties
Mechanism of Action:
- Competes with aldosterone at mineralocorticoid receptors in the distal renal tubules.
- Inhibits sodium reabsorption and promotes potassium retention and diuresis.
Related Compounds:
- Spironolactone (marketed)
- Prorenoic acid (parent compound)
Activity:
- Studied for aldosterone antagonistic activity
- Not pursued for commercial development, possibly due to pharmacokinetic or efficacy issues compared to alternatives
Occurrences and Development
Natural Occurrence: Does not occur naturally; it is a fully synthetic compound
Synthesis: Derived from steroidal precursors through chemical modification to introduce:
- The spirolactone ring
- Carboxylic acid side chain (neutralized with potassium)
Usage: Investigational only; never reached the market