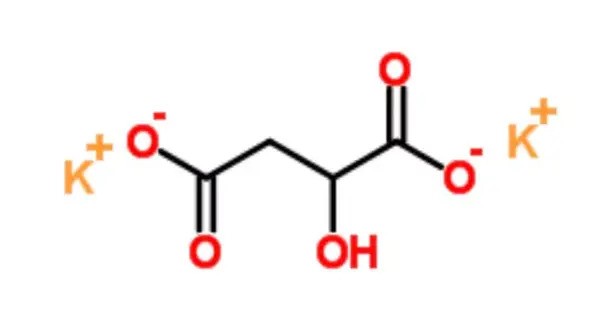
Potassium malate is a compound with formula K2(C2H4O(COO)2). It is the potassium salt of malic acid. It is an organic acid commonly found in fruits such as apples and pears. It is typically used as a potassium supplement and can be found in various dietary supplements, especially for those who may need to increase their potassium intake.
As a food additive, it has the E number E351. It is used as acidity regulator or acidifier for use in, for example, canned vegetables, soups, sauces, fruit products, and soft drinks. It also acts as an antioxidant and a food flavoring agent.
It is an important compound in the transport of nitrate from the roots of a plant to the leaves of the plant. Potassium malate is the salt that transports from the leaves to the root. At the root, the potassium malate oxidizes to potassium carbonate, then is converted to potassium nitrate by soil nitrate and transported back to the leaves.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C4H4K2O5
- Molar mass: 210.268 g·mol−1
- Appearance: White crystalline powder or granules.
- Solubility: Soluble in water, forming a mildly acidic solution due to the presence of the malate anion.
- Taste: Slightly sour, similar to malic acid, due to the nature of the malate ion.
- pH: When dissolved in water, potassium malate forms a slightly basic solution with a pH above 7, but not very high.
- Stability: It is generally stable under normal conditions but can degrade under extreme conditions, such as high heat or strong acids.
- Reactivity: It can participate in reactions that involve the potassium ion or the malate ion.
Occurrences
In Nature: Potassium malate can be found in trace amounts in various fruits and vegetables, particularly those rich in malic acid, such as apples, cherries, and grapes. Malic acid itself, the precursor of potassium malate, is produced in the body as part of cellular metabolism (in the citric acid cycle).
In Plants: It is not typically found in its pure form in nature, but potassium and malate ions are present in many plant tissues, often as part of the plant’s nutrient system.
Industrial and Agricultural Occurrence: It is used as a supplement or fertilizer additive in some agricultural applications, especially as a source of potassium and malic acid. The compound may also be used to fortify foods and beverages with potassium and improve their mineral content.
Applications
Potassium malate is often used in the context of:
- Electrolyte balance – Potassium helps regulate fluid and electrolyte balance in the body.
- Muscle function – It may help prevent muscle cramps, especially for athletes or individuals involved in heavy physical activity.
- Energy production – Thanks to the malate component, it could support energy production processes in cells.
In some cases, potassium malate is used to treat potassium deficiencies, though it should be used with caution as excessive potassium intake can lead to hyperkalemia, a dangerous condition. Always consult with a healthcare provider before using potassium supplements.
Safety Considerations
- Ingestion: Potassium malate is generally considered safe in normal amounts as part of food or dietary supplements. However, excessive potassium intake can cause hyperkalemia, which can lead to serious health issues.
- Handling: While handling potassium malate in a laboratory or industrial setting, care should be taken to avoid excessive dust inhalation or contact with eyes.