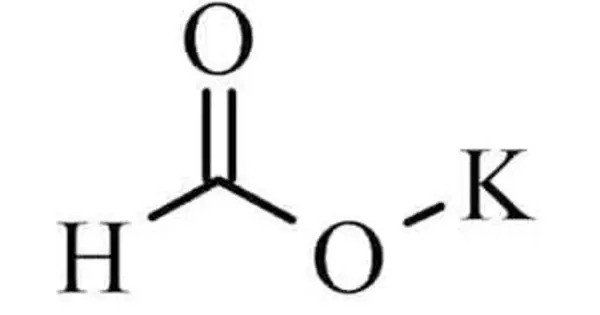
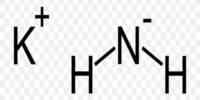
Potassium formate, HCO2K, HCOOK, or KHCO2, is the potassium salt of formic acid. This strongly hygroscopic white solid is an intermediate in the formate potash process for the production of potassium. It consists of potassium (K) and the formate ion (HCO₂⁻), which is derived from formic acid (HCOOH).
Potassium formate has also been studied as a potential environmentally friendly deicing salt for use on roads. It has also been suggested for use in a less corrosive liquid desiccant. A 52% solution of potassium formate has a freezing point of −60 °C (−76 °F). Potassium formate brines are sometimes used for heat transfer, despite being much more corrosive than many other liquid coolants, especially to zinc and aluminum but even to many steels, though some formulations are compatible with aluminum and steels.
Properties
- Chemical formula: CHKO2
- Molar mass: 84.115 g·mol−1
- Appearance: Colorless deliquescent crystals
- Density: 1.908 g/cm3
- Melting point: 167.5 °C (333.5 °F; 440.6 K)
- Boiling point: Decomposes
- Solubility in water: 32.8 g/100 mL (0 °C), 331 g/100 mL (25°C), 657 g/100 mL (80 °C)
- Solubility: soluble in alcohol, insoluble in ether
Occurrences
- Natural Sources: It is not typically found in nature in its pure form, but formic acid (the precursor to potassium formate) is produced by various biological processes. It’s commonly found in the bodies of some insects, like ants, and in the stings of bees.
- Synthesis: It is most commonly produced synthetically by reacting potassium hydroxide (KOH) with formic acid (HCOOH), or by neutralizing potassium carbonate (K₂CO₃) with formic acid.
Industrial uses
Potassium formate is widely used in the oil and gas industry, especially as a drilling fluid and in enhanced oil recovery (EOR) processes due to its effectiveness in improving fluid properties in high-temperature environments. It also finds use in other chemical processes and as an antifreeze in certain applications.
Potassium formate is typically used as a deicing agent on roads and in industrial applications, including as a buffer solution, in agriculture, and in certain chemical reactions. Since 1995, potassium formate has been increasingly used in aqueous Drilling fluids to increase density, stabilize the hole, and improve drilling performance.