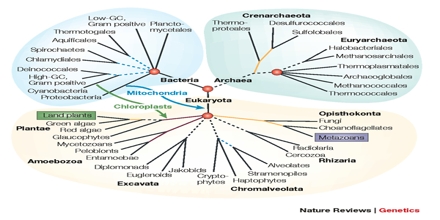
Phylogenomics forces information by evaluating entire genomes or at least large portions of genomes. Phylogenetics measures up and analyzes the actual sequences of solitary genes, or a few genes, as well several other types of data. Four major areas are categorized as phylogenomics: Prediction of gene function, Establishment and clarification of evolutionary relationships, Gene family evolution, Prediction and retracing lateral gene transfer.
Phylogenomics