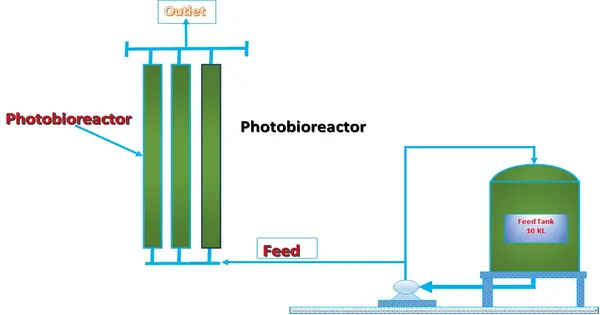
A photobioreactor (PBR) is a device that harnesses light energy to cultivate photosynthetic organisms, typically microalgae, cyanobacteria, or other photosynthetic microorganisms, for various purposes such as biofuel production, wastewater treatment, carbon capture, and production of high-value compounds like pigments or pharmaceuticals. It refers to any cultivation system designed for growing photoautotrophic organisms using artificial light sources or solar light to facilitate photosynthesis. Photobioreactors are typically used to cultivate microalgae, cyanobacteria, and some mosses.
These reactors provide controlled conditions for the growth of photosynthetic organisms, including regulation of light intensity, temperature, pH, and nutrient availability. They are often cylindrical or tubular in shape, with transparent walls to allow light penetration. The design can vary widely depending on the specific application and scale of operation.
Photobioreactors can be open systems, such as raceway ponds, which rely upon natural sources of light and carbon dioxide. Closed photobioreactors are flexible systems that can be controlled to the physiological requirements of the cultured organism, resulting in optimal growth rates and purity levels.
Photobioreactors can be operated in open or closed systems. Open systems are typically ponds or raceways, where microorganisms are exposed directly to sunlight but are more susceptible to contamination and have limited control over environmental conditions. Closed systems, on the other hand, offer more control over growth conditions, but require artificial light sources, which can increase energy costs.
Applications
Photobioreactors are typically used for the cultivation of bioactive compounds for biofuels, pharmaceuticals, and other industrial uses. These offer a promising solution for sustainable production of biomass and valuable products using photosynthetic microorganisms, with ongoing research aiming to optimize their efficiency and scalability for various applications.
Advantages
These reactors are used in various industries for different purposes:
- Biofuel Production: Algae cultivated in photobioreactors can be used to produce biofuels such as biodiesel and bioethanol.
- Nutraceuticals and Pharmaceuticals: Some microalgae species are rich sources of valuable compounds like omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and pigments that have applications in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries.
- Wastewater Treatment: Algae can be used to treat wastewater by absorbing nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, thereby reducing pollution.
- Carbon Capture and Sequestration: Algae can consume carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, making photobioreactors potentially useful for carbon capture and sequestration efforts.
- Food and Feed Additives: Certain microalgae species are cultivated in photobioreactors for the production of food additives, colorants, and nutritional supplements.
Photobioreactors offer several advantages over traditional open pond systems, including better control over environmental conditions, higher productivity, and reduced contamination risks. However, they also have higher capital and operating costs.