Phosphoramidates (also known as amidophosphates) are phosphorus compounds that are structurally related to phosphates (or organophosphates) by the substitution of an OR for an NR2. This is a class of organic compounds that have a phosphorus atom that is covalently bound to one or more nitrogen atoms. They are phosphoramidic acid derivatives O=P(OH)(NR2)2, O=P(OH)2(NR2). They are phosphoric acid (H3PO4) derivatives in which one or more of the hydroxyl (-OH) groups have been replaced with amino (-NH2) or similar groups.
Because of their unique features, phosphoramidates are frequently used in a variety of chemical and biological applications. It’s a phosphate with two of its OH groups replaced by NR2 groups, resulting in a species with the generic formula O=P(OH)(NH2)2. The phosphoric triamides (O=P(NR2)3), often known as phosphoramides, are formed by substituting all three OH groups.
Examples
Two examples of natural phosphoramidates are phosphocreatine and the phosphoramidate formed when histidine residues in histidine kinases are phosphorylated. An example of a phosphorodiamidate is morpholino which is used in molecular biology.
Here are some key points about phosphoramidates:
- Structure: Phosphoramidates have a central phosphorus atom (P) bonded to nitrogen atoms (N) and other substituent groups. The general formula for a simple phosphoramidate is R1PO(NR2R3)2, where R1, R2, and R3 can be different organic groups.
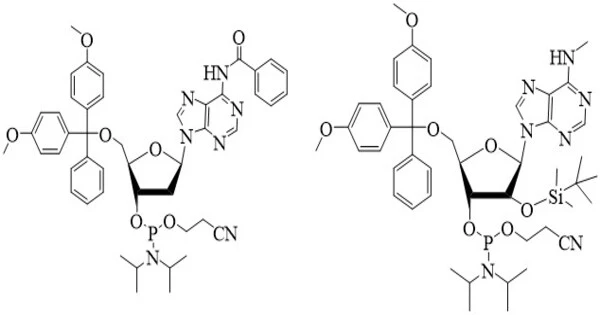
- Synthesis: Phosphoramidates can be synthesized through various methods, including the reaction of phosphorus oxychloride (POCl3) or phosphoryl chloride (POCl3) with primary or secondary amines. Other methods involve the use of phosphoramidite reagents in solid-phase synthesis.
- Prodrugs: Phosphoramidate prodrugs are compounds designed to improve the pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of certain drugs. These prodrugs are often more stable or soluble than the parent drug and can be converted to the active form in the body.
Applications:
- Phosphoramidates are important intermediates in the synthesis of nucleoside analogs and phosphoramidate prodrugs, which are used in antiviral and anticancer drug development.
- They are used in DNA and RNA synthesis as phosphoramidite derivatives, which are crucial for solid-phase synthesis methods.
- Phosphoramidate analogs of nucleotides are used in research on nucleic acid structure and function.
- Some phosphoramidates have been investigated for their potential as flame retardants and as components in materials science.
Biological Importance
Phosphoramidates have been studied in molecular biology for their ability to change DNA and RNA sequences, which could be valuable in gene therapy and other genetic engineering applications.
Phosphoramidates have a wide range of uses in organic chemistry and biology, making them an important family of chemicals in a wide range of scientific and industrial disciplines. Their adaptability and capacity to be modified for specific objectives add to their importance in R&D.