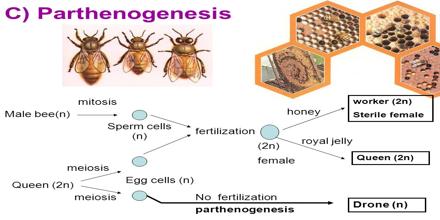
This article focus on Parthenogenesis, which is a type of asexual reproduction in which a female gamete or egg cell develops into an individual without fertilization. It is an adaptive strategy to ensure the reproduction of organisms when conditions are not favorable for sexual reproduction. The term is sometimes used inaccurately to describe reproduction modes in hermaphroditic species that can reproduce by themselves because they contain reproductive organs of both sexes in a single individual’s body. Parthenogenesis occurs naturally in many plants, some invertebrate animal species including nematodes, water fleas, some scorpions, aphids, some bees, some Phasmida and parasitic wasps and a few vertebrates, such as some fish, amphibians, reptiles and very rarely birds.
Parthenogenesis