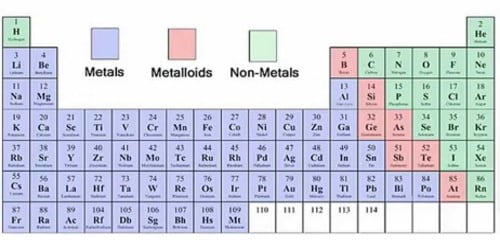
Nonmetal or non-metal is a chemical element that does not have the properties of a metal. These elements are omnipresent and essential for life. Some are gases including – hydrogen, helium, oxygen, nitrogen, fluorine, neon or radon and many others. An example of a solid that is a nonmetal is sulfur. It is yellow and not shiny at all. An example of a liquid that is a nonmetal is bromine. It is red. A nonmetal is also a good insulator for heat and cold. Usually, gases or brittle solids are non-metals. Elements on the periodic table can be classified as a metal, semimetal, or non-metal. The nonmetals are in a minority on the periodic table, mostly located on the right-hand side of the periodic table. They usually have 4, 5, 6 or 7 electrons in their outermost shell.
A nonmetal is simply an element that does not display the properties of a metal. Only 17 elements on the periodic table are nonmetal elements, yet they make up most of the matter in the universe and most of us living things! Five times more elements are metals than nonmetals. The 17 nonmetal elements are – hydrogen, helium, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, neon, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, argon, selenium, bromine, krypton, iodine, xenon, and radon. Nonmetals have high ionization energies and electronegativities. They are generally poor conductors of heat and electricity.
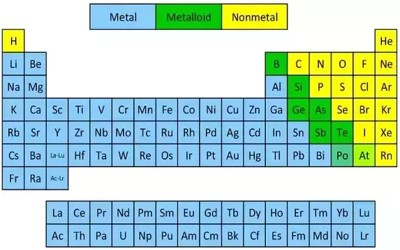
Physical Properties of Non-Metals –
- They are not lustrous as they do not have any shiny appearance.
- They are not sonorous and do not produce a deep ringing sound when they are hit with another material.
- They are also bad conductors of heat and electricity except for graphite.
- Lower melting point and boiling points.
Chemical Properties of Non-Metals –
- Non-metal does not react with water but it is usually very reactive in air, which is why some of them are stored in water.
- None of the non-metals is known to react with acids.
- The reaction between non-metals and bases is a very complex one.
- Oxides of non-metals are formed when it reacts with oxygen.
However, nonmetals are abundant and important. Most nonmetals have the ability to gain electrons easily. Two of the nonmetals—hydrogen, and helium – make up over 99 percent of the observable Universe, and one—oxygen—makes up close to half of the Earth’s crust, oceans, and atmosphere. Living organisms are also composed almost entirely of nonmetals, and nonmetals form many more compounds than metals.