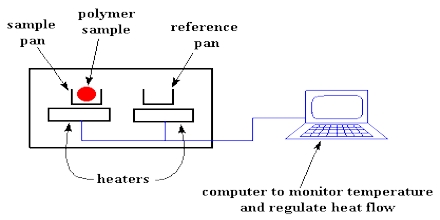
Differential scanning calorimetry or DSC is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to boost the temperature of your sample and referrals is measured as being a function of temp. Both the test and reference are generally maintained at nearly identical temperature throughout the experiment. Types of DSC: Power compensated DSC, keeps power supply constant and Heat flux DSC, keeps heat flux constant.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry