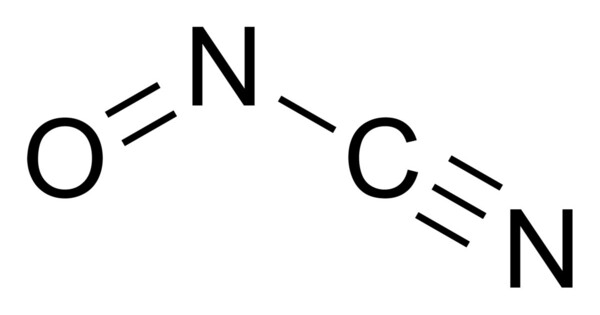
Nitrosyl cyanide, a blue-green gas, is the compound with the molecular formula ONCN. The compound has been invoked as a product of the oxidation of cyanamide catalyzed by the enzyme glucose oxidase. It is a reactive compound due to the presence of both the nitrosyl group (NO) and the cyanide group (CN). It can react with various nucleophiles and electrophiles.
Properties
- Molecular Formula: NO-CN
- Molecular Weight: Approximately 63.03 g/mol
- Appearance: Typically a colorless to pale yellow gas or liquid.
- Boiling Point: -1.5 °C (29.3 °F)
- Density: About 1.14 g/cm³ (liquid form)
- Solubility: It is soluble in organic solvents like alcohols and ethers but is less soluble in water.
Structure, synthesis, reactivity
The structure of nitrosyl cyanide is planar. It is strongly bent at the internal nitrogen, analogous to the structure of nitrosyl chloride. The C-N-O angle is 113°. The NCN angle is 170°.
The compound can be created by the reaction of nitrosyl chloride and silver cyanide at low temperatures. It is not typically isolated, but trapped by Diels-Alder reactions, e.g. with butadiene. Cycloadditions occur across the N=O bond. It forms a reversible adduct with 9,10-dimethylantracene.
Uses
- Industrial Applications: Nitrosyl cyanide is used in organic synthesis, especially for introducing nitrosyl and cyanide groups into organic molecules.
- Chemical Research: It serves as a reagent in chemical research and can be used to study the behavior of nitrosyl and cyanide groups in different chemical environments.
- Catalysis: It can be used in some catalytic processes due to its reactivity.
Safety
- Toxicity: Nitrosyl cyanide is highly toxic and should be handled with extreme caution. It can release toxic gases, including hydrogen cyanide, upon decomposition.
- Precautions: Proper protective equipment and ventilation are necessary when working with this compound.