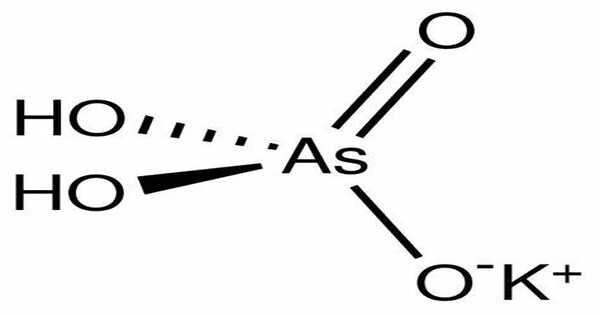
Monopotassium arsenate is the inorganic compound with the formula KH2AsO4. It is the monobasic salt of arsenic acid (H₃AsO₄), meaning it contains one potassium (K⁺) ion and one dihydrogen arsenate (H₂AsO₄⁻) ion. A white solid, this salt is used to prepared other arsenic-containing compounds, mainly pesticides. It is prepared by calcining arsenic oxide and potassium nitrate, followed by extraction with water. It is used in agriculture and industry as a fungicide, herbicide, or wood preservative, though now largely restricted or banned due to toxicity
Relevant acid-base equilibria for aqueous solutions of this diprotic acid derived from arsenic acid are as follows:
H3AsO4 + H2O ⇌ H2AsO−4 + H3O+ (pKa1 = 2.19)
H2AsO−4 + H2O ⇌ HAsO2−4 + H3O+ (pKa2 = 6.94)
Properties
- Chemical formula: AsH2KO4
- Molar mass: 180.032 g·mol−1
- Appearance: white solid
- Density: 2.867 g/cm3
- Melting point: 288 °C (550 °F; 561 K)
- Solubility: Soluble in water
- Stability: Stable under normal conditions, but toxic and environmentally hazardous due to arsenic content
Chemical Behavior
- Acidity: Slightly acidic due to the presence of two acidic hydrogen atoms
- Thermal Decomposition: Upon heating, it decomposes to release arsenic oxides and other potassium salts
- Reactivity: Reacts with strong acids and bases; incompatible with strong oxidizers
Natural Occurrence
Rarity in Nature: Does not commonly occur as a pure mineral
Possible Sources: Can be found as a result of secondary mineral formation in arsenic-rich environments Might appear in oxidized zones of arsenic-containing mineral deposits, though more often in hydrated or mixed forms Related arsenates like scorodite (FeAsO₄·2H₂O) are more commonly encountered
Uses
- Used in chemical research
- Sometimes as a reagent in laboratory settings
- Historically used in pesticides or herbicides (now mostly discontinued due to toxicity)
Safety and Handling
- Highly toxic: Can be fatal if swallowed or inhaled
- Carcinogen: Contains arsenic, a known human carcinogen
- Requires protective equipment when handling, and strict environmental controls