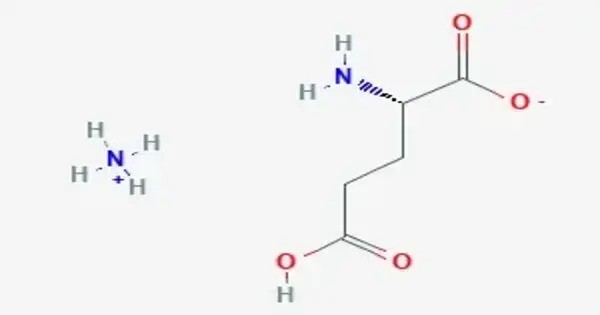
Monoammonium glutamate is a compound with formula NH4C5H8NO4. It is an ammonium acid salt of glutamic acid. Like its sodium counterpart (monosodium glutamate, MSG), monoammonium glutamate functions as a flavor enhancer due to the presence of the glutamate ion, which is responsible for the umami taste — one of the five basic taste sensations.
This compound appears as a white, crystalline powder that is soluble in water and has a savory or meaty flavor. It is less commonly used than MSG but serves similar purposes in food production, especially in low-sodium formulations, vegetarian or organic products, or applications avoiding sodium-based additives.
It has the E number E624 and is used as a flavor enhancer. Its E number in food additives classification is E624, and it is primarily used in processed meats, soups, snacks, and seasonings. Monoammonium glutamate is also studied for potential use in specialized industrial or pharmaceutical applications.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C5H12N2O4
- Molar mass: 164.161 g·mol−1
- Appearance: Typically a white crystalline powder (if isolated in pure form)
- Solubility: Soluble in water
- pH (aqueous solution): Slightly acidic to neutral, depending on concentration
Natural Occurrence
- Rarely found in nature in its free salt form.
- May transiently form in environments rich in ammonia and free glutamic acid (e.g., decaying protein matter, soil microbiomes).
Industrial / Laboratory Production
Formed by neutralizing glutamic acid with ammonium hydroxide (NH₄OH).
Reaction: Glutamic acid (C₅H₉NO₄)+NH₄OH→Monoammonium glutamate (C₅H₁₀N₂O₄)+H
Biochemical Relevance
Ammonium ions and glutamate are key intermediates in nitrogen metabolism, particularly in the glutamine synthetase/glutamate synthase (GS/GOGAT) pathway. However, the exact compound “monoammonium glutamate” is not a recognized metabolite in standard biochemistry databases.
Applications
Monoammonium glutamate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) when used in accordance with good manufacturing practices. However, like other glutamate salts, it may cause mild reactions (e.g., headache or flushing) in sensitive individuals, sometimes referred to as “Chinese Restaurant Syndrome,” though scientific evidence supporting this is limited.
- Food Industry (theoretical): Could be explored as an umami flavor enhancer, like MSG, though not commonly used.
- Agriculture: Ammonium-based amino acid salts may be explored in foliar fertilizers or biostimulants.
- Research: Used in studies involving nitrogen assimilation or amino acid transport.
Safety and Handling
- Toxicity: Expected to be low, similar to MSG and glutamic acid.
- Handling: Use appropriate lab safety procedures (gloves, goggles) when handling powdered or concentrated forms.