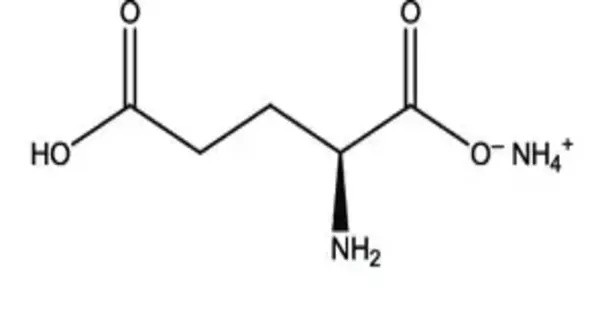
Monoammonium glutamate is a compound with formula NH4C5H8NO4. It is an ammonium acid salt of glutamic acid. It is a chemical compound that is the monoammonium salt of glutamic acid, an amino acid. It is structurally related to monosodium glutamate (MSG) but uses ammonium (NH₄⁺) instead of sodium (Na⁺) as the cation. It is the monoammonium salt form of the amino acid glutamic acid, in which only one of the two carboxylic acid groups is neutralized by ammonia (NH₃).
It has the E number E624 and is used as a flavor enhancer.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C5H12N2O4
- Molar mass: 164.161 g·mol−1
- Solubility: Soluble in water
- Appearance: Typically white crystalline powder
- Stability: Stable under normal conditions
- pH (1% soln): Slightly acidic to neutral
- Taste: Like MSG, it has umami (savory) flavor properties, due to the presence of glutamate.
Occurrence
- Not commonly found in nature in isolated form.
- Formed as an intermediate or derivative in biochemical or industrial processes involving glutamic acid or ammonia.
- May be present transiently in fermentation processes involving amino acid metabolism.
Uses
It can theoretically be used as a flavor enhancer, though it is much less common than MSG. While MSG is widely used in the food industry, monoammonium glutamate is not commonly used commercially. It might appear in experimental or niche food formulations, biochemical research, or nutritional studies, but is not a major additive.
- Food industry (limited): Related compounds such as monosodium glutamate (MSG) are widely used as flavor enhancers, but monoammonium glutamate itself is not a common additive.
- Chemical or biochemical research: Used as a model compound for studying amino acid salt behavior or ammonium ion interactions.
- Nutritional supplements or animal feed: Potentially used in some formulations as a nitrogen source or for glutamate supplementation.
Safety and Handling
- Generally regarded as low toxicity, similar to glutamic acid and ammonium salts.
- Handle with standard laboratory precautions.
- Excessive intake (as with any glutamate source) may have excitatory neurological effects in sensitive individuals.