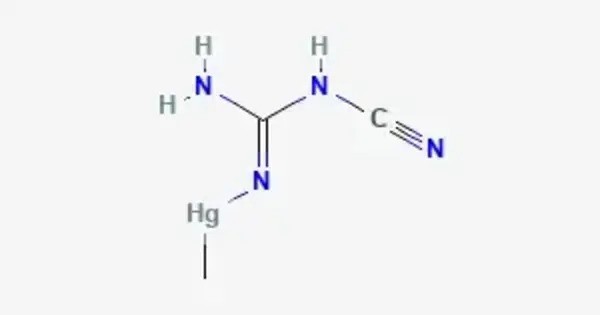
Methylmercuric dicyanamide is a chemical compound used as a fungicide for crops such as cereals, cotton, flax, sorghum, and sugar beets. It is an organomercury compound historically used as a fungicide. As of 1998, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency listed it as an unregistered pesticide in the United States. It is a colorless crystalline solid with the chemical formula C₃H₆HgN₄ and IUPAC name 1-cyano-3-(methylmercurio)guanidine. Although named as a dicyanamide, the major organic structure is a 2-cyanoguanidino group.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C3H6HgN4
- Molar mass: 298.70 g/mol
- Molecular Weight: 298.72 g/mol
- Melting Point: Approximately 156°C (313°F)
- Vapor Pressure: 6.5 × 10⁻⁵ mmHg at 35°C
- Solubility: Data unavailable
- Flash Point: Data unavailable
- Boiling Point: Data unavailable
Occurrences
Methylmercuric dicyanamide was employed as a fungicide for treating seeds, soil, and turf, particularly for crops like cereals, sorghum, sugar beets, cotton, and flax . However, it is not registered as a pesticide in the U.S. Its use has been discontinued in many countries due to its high toxicity and environmental concerns.
Toxicity and Health Hazards
This compound is extremely toxic to humans. The probable lethal dose ranges from 5 to 50 mg/kg of body weight. Symptoms of poisoning include:
- Skin irritation, blisters, and dermatitis
- Neurological effects such as confusion, irritability, seizures, hallucinations, and memory loss
- Mercury vapor exposure can cause severe pulmonary damage and gingivitis
Exposure may occur through ingestion of treated seeds or consumption of animals that have ingested the fungicide .
Environmental Impact
Methylmercuric dicyanamide poses significant ecological risks. It is highly toxic to birds and mammals, with potential reproductive and developmental effects. The compound’s persistence in the environment and bioaccumulation in food chains contribute to its environmental hazards.