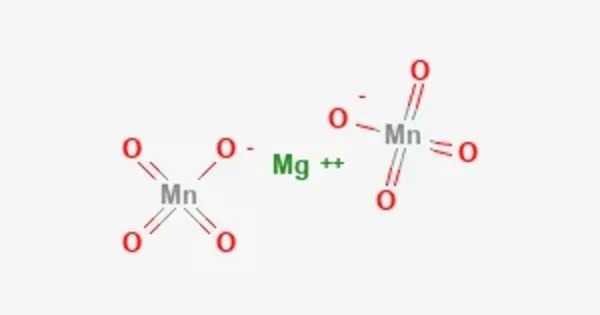
Magnesium permanganate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Mg(MnO4)2. It can be used as an oxidant. Known for its strong oxidizing properties, this dark purple crystalline solid is less common than other permanganates such as potassium permanganate but shares many similar chemical behaviors. It is typically used in specialized oxidation reactions, water treatment, and occasionally in laboratory synthesis due to its ability to release oxygen.
Magnesium permanganate is valued for its reactivity and its relatively high solubility in water compared to some other permanganate salts, making it useful in aqueous applications.
Properties
- Chemical formula: Mg(MnO4)2
- Solubility in water: soluble
- Appearance: Usually appears as a dark purple or violet crystalline solid due to the intense color of the permanganate ion.
- Solubility: Soluble in water, like other permanganates.
- Oxidizing Agent: Strong oxidizer due to the presence of the MnO₄⁻ ion.
- Stability: Less stable than potassium permanganate; can decompose over time, especially in humid or hot conditions.
Preparation
Magnesium permanganate hexahydrate was prepared by E. Mitserlich and H. Aschoff by reacting barium permanganate with magnesium sulfate:
MgSO4 + Ba(MnO4)2 → Mg(MnO4)2 + BaSO4
It can be obtained by the reaction of magnesium chloride and silver permanganate:
MgCl2 + 2AgMnO4 → Mg(MnO4)2 + 2AgCl
The hexahydrate Mg(MnO4)2·6H2O can be crystallized from the solution, which is slightly hygroscopic. The anhydrous form can be obtained by decomposing the hexahydrate by heating it.
Chemical properties
Magnesium permanganate hexahydrate is a blue-black solid. It decomposes at 130 °C with the evolution of oxygen in an autocatalytic decomposition process. The tetrahydrate decomposes above 150 °C. The crystals are practically insoluble in carbon trichloride, carbon tetrachloride, benzene, toluene, nitrobenzene ether, ligroin and carbon disulfide, but soluble in pyridine and glacial acetic acid. It dissolves in water and dissociates completely in dilute solutions.
Applications
Magnesium permanganate is used in various branches of industry and technology, such as:
- a wood impregnation agent.
- an additive in tobacco filters.
- as a catalyst in the air oxidation of toluene to benzoic acid and in proteome research.
- Oxidizing Agent: Employed in chemical reactions where a strong oxidizer is needed.
- Disinfection and Water Treatment: Occasionally used in similar ways to potassium permanganate, though less common.
- Analytical Chemistry: May be used in redox titrations, though again, potassium permanganate is more typical.
Natural Occurrence
- Does not occur naturally as a mineral due to instability.
- Permanganate salts are synthesized; they are not found in significant amounts in nature.
- Manganese oxides (MnO₂) are the naturally occurring forms of manganese in the +4 oxidation state.
Safety Considerations
- Oxidizer: Can react violently with reducing agents, organic materials, or flammable substances.
- Toxicity: Permanganates can be toxic if ingested or inhaled in dust form; they are also corrosive to skin and eyes.