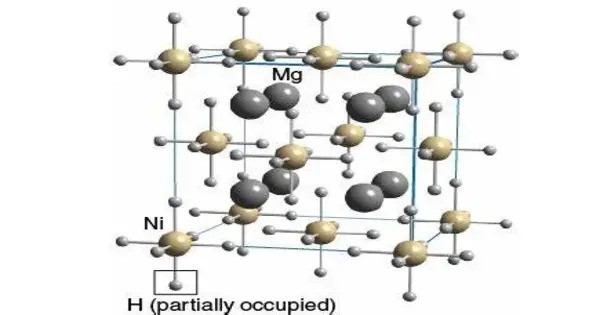
Magnesium nickel hydride is the chemical compound Mg2NiH4. It is a metal hydride compound that’s particularly interesting in the field of hydrogen storage materials. It contains 3.6% by weight of hydrogen and has been studied as a potential hydrogen storage medium.
Properties
- Chemical formula: Mg2NiH4
- Molar mass: 111.33 g/mol
- Appearance: black/brown
- Density: 2.71 g/cm3
- Crystal Structure: Tetragonal (for the high-temperature β-phase) and monoclinic (for the low-temperature α-phase)
- Color: Ranges from bronze (metallic alloy) to gray-black (hydride)
- Decomposition Temperature: ~250–300°C (releases H₂ upon heating)
- Thermal Stability: Stable up to its decomposition temperature in inert atmosphere
Formation and Hydrogenation Process
- Mg₂Ni alloy reacts with hydrogen gas at elevated temperatures (~250–300°C) and pressures (several bars) to form Mg₂NiH₄.
- Hydrogenation is reversible, making it useful for solid-state hydrogen storage.
- The hydrogenation/dehydrogenation kinetics can be improved by nanostructuring or doping.
Crystal Phases
- α-Phase (Low Temp): Monoclinic; stable below ~210°C.
- β-Phase (High Temp): Tetragonal; stable above ~210°C.
These phase changes are important for its hydrogen storage behavior and can impact reaction kinetics.
Occurrence
- Not naturally occurring in the Earth’s crust — it’s synthesized in the lab or industry.
- The Mg₂Ni alloy is prepared by melting elemental magnesium and nickel together or using mechanical alloying.
- Hydrogenation is done in reactors under controlled temperature and pressure.
Applications
- Hydrogen storage: It’s been studied as a promising material for solid-state hydrogen storage.
- Fuel cells: Potential use in mobile or stationary hydrogen energy systems.
- Battery materials: Research into its electrochemical properties is ongoing.