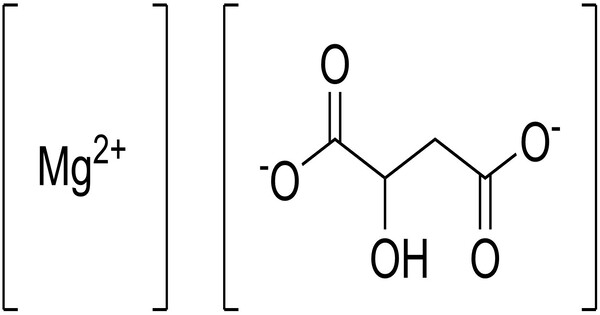
Magnesium malate, the magnesium salt of malic acid, is a mineral supplement often used for nutritional concerns. It is represented by the chemical formula C4H4MgO5 and has a molecular weight of 156.376 g/mol. Magnesium malate is discussed as being a more bioavailable form of magnesium, along with other forms such as citrate and glycinate.
Magnesium malate is a dietary supplement that combines magnesium with malic acid. Magnesium is an essential mineral involved in numerous bodily functions, including muscle and nerve function, blood sugar regulation, and bone health. Malic acid is an organic compound found in various fruits and is known for its role in the Krebs cycle, which helps generate energy in cells.
Properties
Magnesium malate is soluble in water. This solubility is one of the reasons it’s used in dietary supplements, as it can be easily absorbed by the body. In its pure form, it may appear as a white or off-white powder. It’s generally used in this powdered form or as a component in dietary supplements. It is relatively stable under normal conditions. It does not react violently with water or air, which makes it suitable for use in various applications.
- Chemical formula: C4H4MgO5
- Molar mass: 156.376 g·mol−1
Some potential benefits of magnesium malate include:
- Energy Production: Malic acid can help improve energy production at the cellular level, which might help reduce fatigue.
- Muscle Function: Magnesium is crucial for muscle relaxation and function, and magnesium malate may help with muscle cramps and soreness.
- Pain Relief: Some people use magnesium malate to help manage fibromyalgia symptoms and chronic pain, although more research is needed in this area.
Occurrences
- Dietary Supplements: Magnesium malate is commonly used as a dietary supplement. It provides both magnesium and malic acid, which are beneficial for various bodily functions. Magnesium supports muscle and nerve function, while malic acid plays a role in energy production.
- Natural Sources: Magnesium malate does not occur widely in nature in its pure form. Instead, magnesium and malic acid are found in various natural sources. Magnesium is present in foods such as nuts, seeds, and leafy green vegetables, while malic acid is found in fruits like apples.
Industrial Uses
In addition to dietary supplements, magnesium malate might be used in some industrial applications due to its properties, though it’s less common compared to other magnesium compounds.
Health Implications
Magnesium malate is noted for its good bioavailability, which means it is efficiently absorbed and utilized by the body. This makes it a popular choice for supplementation, particularly for individuals with magnesium deficiency.
Supplementing with magnesium malate may help with various health issues, including muscle pain, fatigue, and certain types of headaches. Malic acid is also believed to play a role in improving exercise performance and reducing muscle soreness.
Side Effects
While generally considered safe, excessive intake of magnesium malate can lead to gastrointestinal issues such as diarrhea. It’s important to follow recommended dosages and consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.