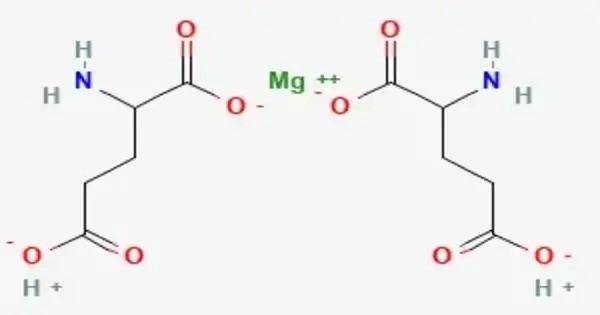
Magnesium diglutamate is a compound with formula Mg(C5H8NO4)2. It is a magnesium acid salt of glutamic acid. It is a chemical compound that consists of magnesium and glutamic acid residues (specifically, the anionic form of glutamic acid, known as glutamate). It’s essentially a magnesium salt of glutamic acid, and its structure involves two glutamate molecules bound to a single magnesium ion.
It has the E number E625 and is used in foods as a flavor enhancer. It is not as widely known or used as sodium glutamate (like monosodium glutamate or MSG), but it has similar biochemical relevance and properties.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C10H16MgN2O8
- Molar mass: 316.549 g·mol−1
- Melting point: Tetrahydrate: 130 to 135 °C (266 to 275 °F; 403 to 408 K) (decomposes)
- Appearance: White or off-white crystalline powder (typical for amino acid salts)
- Solubility: Water: Soluble; Organic solvents: Poorly soluble (common for amino acid salts)
- Taste: Umami, similar to MSG, due to the glutamate component
Natural Occurrence
- Not commonly found in pure form in nature.
- Magnesium and glutamic acid are both naturally abundant:
- Magnesium in minerals and biological systems
- Glutamic acid in proteins (it’s a common amino acid)
- It may form naturally in some metabolic or digestive processes, but it’s not a primary dietary component or naturally occurring mineral.
Uses
- Food industry (potential): As a flavor enhancer like MSG, though it’s not common or commercially popular.
- Supplements: Could theoretically be used to deliver both magnesium and glutamate for neurological or muscle health, but this is rare.
- Research: Sometimes used in biochemical studies to explore neurotransmitter behavior (glutamate is a key neurotransmitter).