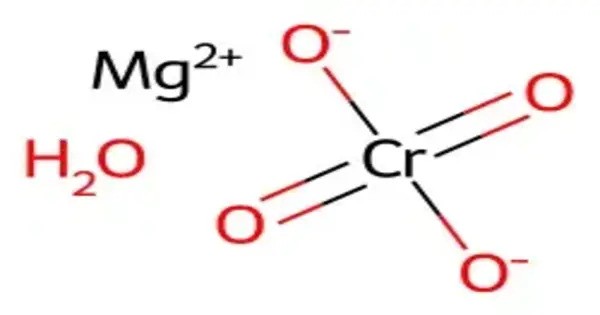
Magnesium chromate is a chemical compound, with the formula MgCrO4. It is an inorganic salt consisting of magnesium cations (Mg²⁺) and chromate anions (CrO₄²⁻). Magnesium chromate is typically a yellow, crystalline substance and is used in a variety of applications, particularly in industrial and chemical processes. It is a yellow, odorless, water-soluble salt with several important industrial uses. This chromate can be manufactured as a powder.
Properties
- Chemical formula: MgCrO4
- Molar mass: 140.297 g·mol−1
- Appearance: Yellow solid
- Solubility in water: soluble
- Reactivity: It is an oxidizing agent, so it can react with reducing agents.
History
Before 1940, the literature about magnesium chromate and its hydrates was sparse, but studies starting in that year looked at its properties and solubility.
Occurrence
Magnesium chromate does not naturally occur in large quantities like other minerals, but it can form under certain geological conditions. In nature, it is generally found in certain chromite ores, particularly in regions where there are high concentrations of chromium, such as in:
- Chromite deposits: Magnesium chromate can form in deposits where magnesium-rich minerals are found alongside chromium ores, especially in volcanic rocks and metamorphic environments.
- Synthetic production: The most common occurrence of magnesium chromate is through synthetic methods, especially in industries that produce it for use in various applications, such as pigments or corrosion-resistant coatings.
Uses
It is available commercially in a variety of powders, from nanoscale to micron-sized, either as an anhydrous or hydrated form. It is commonly used in the manufacturing of pigments and dyes, especially for yellow coloring. In the past, it was used in corrosion-resistant coatings for steel and as a primer for paints.
Hazards
Magnesium chromate hydrate should be stored at room temperature, and there is no current therapeutic use. It is a confirmed carcinogen, and can cause acute dermititis, and possibly kidney and liver damage if inhaled, so it should be treated as a hazardous waste. Chromium compounds, including magnesium chromate, are considered hazardous. Chromium (VI), which is present in magnesium chromate, is a known carcinogen, and exposure should be minimized.