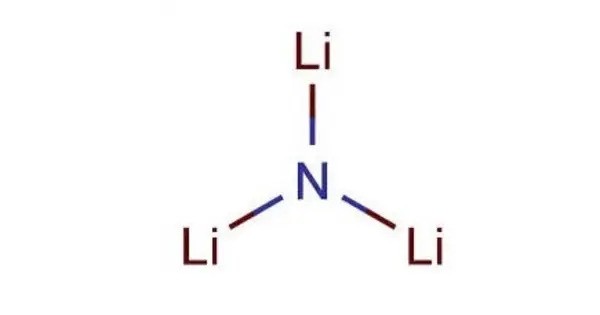
Lithium nitride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Li3N. It is the only stable alkali metal nitride. It is a reddish-pink solid with a high melting point. It is an important material in various advanced technologies, especially in the fields of battery development, energy storage, and materials science.
Properties
Lithium nitride is typically a gray or dark brown solid. It is highly hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the air, which can degrade its properties.
- Chemical formula: Li3N
- Molar mass: 34.83 g·mol−1
- Appearance: Red-purple or reddish-pink crystals or powder
- Density: 1.270 g/cm3
- Melting point: 813 °C (1,495 °F; 1,086 K)
- Solubility in water: reacts
Preparation and handling
Lithium nitride is prepared by direct reaction of elemental lithium with nitrogen gas:[2]
6 Li + N2 → 2 Li3N
Instead of burning lithium metal in an atmosphere of nitrogen, a solution of lithium in liquid sodium metal can be treated with N2.
Lithium nitride must be protected from moisture as it reacts violently with water to produce ammonia:
Li3N + 3 H2O → 3 LiOH + NH3
Applications
- Battery Technology: Lithium nitride is considered an important material in the development of solid-state batteries and advanced energy storage systems. Its role is primarily in improving the performance of electrolytes in lithium-ion batteries or as a component of the anode materials.
- Superconducting Materials: Research has explored the use of lithium nitride in superconducting materials, although this application is still under investigation.
- Lithium Ion Conductors: The high ionic conductivity of lithium nitride makes it a promising candidate for use in lithium-ion conductors for solid-state batteries.
- Nitride Ceramics: Lithium nitride is used in the production of ceramics that require high-temperature stability and resistance to corrosion or oxidation.
Safety Considerations
Lithium nitride should be handled with care due to its reactivity, especially in the presence of moisture or air. Its contact with water generates ammonia gas, which is toxic, and it should be stored in a dry, controlled environment to prevent unwanted reactions.