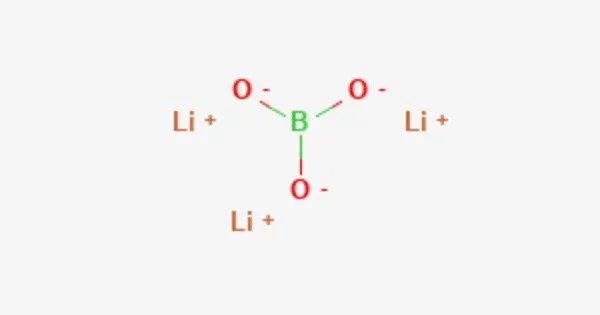
Lithium borate (Li2B4O7) is a chemical compound that consists of lithium and borate ions. It is a compound of lithium, boron, and oxygen. It is a white, odorless, and crystalline solid that is soluble in water and has a melting point of 925°C.
It is commonly used in the production of glasses, ceramics, and semiconductors due to its unique properties such as high melting point, high thermal stability, low thermal expansion coefficient, and good chemical resistance.
Lithium borate has attracted attention in the field of radiation dosimetry, where it is used as a thermoluminescent dosimeter (TLD) material. When exposed to ionizing radiation, lithium borate emits light that is proportional to the radiation dose received. This property makes it useful in measuring radiation doses for medical, industrial, and environmental applications.
Properties
- Physical state: It is a white crystalline solid.
- Melting and boiling point: 845°C, it does not have a distinct boiling point as it decomposes before reaching its boiling point.
- Solubility: It is slightly soluble in water and soluble in acids.
- Density: 2.45 g/cm³.
- Stability: It is stable at room temperature, but it can decompose at higher temperatures.
- Electrical conductivity: It is an insulator at room temperature, but it can conduct electricity when heated or exposed to radiation.
Structure
Its structure consists of a polymeric borate backbone. The Li+ centers are bound to four and five oxygen ligands. Boron centers are trigonal and tetrahedral. It can be used in the laboratory as LB buffer for gel electrophoresis of DNA and RNA. It is also used in the borax fusion method to vitrify mineral powder specimens for analysis by WDXRF spectroscopy.
Application
Lithium borate has various applications, including as a flux in ceramics and glass production, as a catalyst in organic chemistry, and as a component in lithium-ion batteries. It is also used in the analysis of geological samples as a fusion agent, as well as in the production of specialty glasses for radiation shielding and neutron detection.
Lithium borate is also used as a flux in the production of lead-free soldering materials and as a neutron shielding material in nuclear reactors. In addition, it has been studied for its potential use in the development of lithium-ion batteries due to its high lithium ion conductivity.
Overall, lithium borate has a wide range of applications and its unique properties make it a valuable material in various industries.