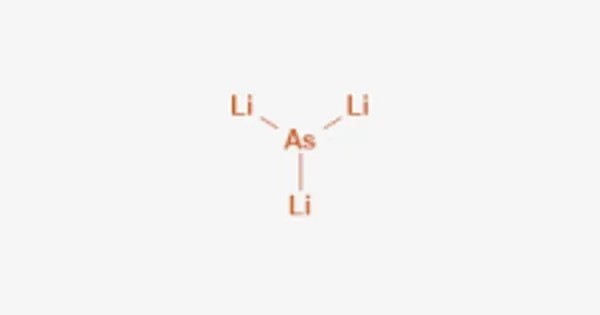
Lithium arsenide describes inorganic compounds with the chemical formula LixAs where x can range from about 0.5 to 3. It is an inorganic compound composed of lithium (Li) and arsenic (As). A common derivative is Li3As, which is prepared by the reduction of arsenic with a solution of lithium in ammonia. It is part of a broader class of lithium-arsenic intermetallic compounds and is of interest in solid-state chemistry and materials science. It can also be produced by heating the elements.
3 Li + As → Li3As
Properties
- Chemical formula: AsLi3
- Molar mass: 95.74 g·mol−1
- Appearance: red-brown
- Density: 3.71 g/cm3
- Crystal Structure: Orthorhombic or other variants depending on synthesis conditions
- Melting Point: Not well-established; thermally unstable at high temperatures
- Electrical Properties: Can exhibit semiconducting or metallic behavior, depending on structure
- Reactivity: Reacts with water and acids; hydrolyzes to form lithium hydroxide and arsine gas (AsH₃)
- Stability: Sensitive to air and moisture; must be handled in inert or vacuum conditions
Natural Occurrence
Lithium arsenide does not occur naturally in significant amounts. It is primarily a laboratory-synthesized compound, produced by direct combination of lithium metal and arsenic at elevated temperatures in an inert atmosphere.However:
- Arsenic naturally occurs in minerals like arsenopyrite (FeAsS), realgar (As₄S₄), and orpiment (As₂S₃).
- Lithium is found in minerals such as spodumene (LiAlSi₂O₆), lepidolite, and petalite.
- Due to the toxicity of arsenic compounds, lithium arsenide is not mined or used on an industrial scale and is mainly confined to academic or experimental settings.
Safety Considerations
- Toxicity: Arsenic compounds are highly toxic. LiAs may release arsine gas (AsH₃) on hydrolysis, which is extremely poisonous.
- Handling: Requires glovebox or inert-atmosphere techniques (e.g., argon glovebox).
- Disposal: Must be disposed of as hazardous waste.
Applications
While lithium arsenide has no major commercial applications, it has niche roles in:
- Materials research
- Quantum materials and semiconductors
- Thermoelectric studies
- Intermetallic chemistry