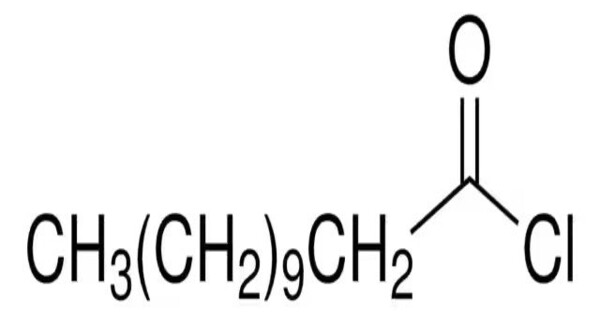
Lauroyl chloride is the organic compound with the formula CH3(CH2)10COCl. It is the acid chloride of lauric acid. Lauroyl chloride is a standard reagent for installing the lauroyl group. It is mainly produced as a precursor to dilauroyl peroxide, which is widely used in free-radical polymerizations. It can react with acids and bases, and its behavior will depend on the specific conditions of the reaction.
Lauroyl chloride is a substrate for diverse reactions characteristic of acid chlorides. With base, it converts to laurone, a ketone with the formula [CH3(CH2)10]2CO. With sodium azide, it reacts to give undecyl isocyanate via a Curtius rearrangement of the acyl azide.
Properties
Cobalt laurate typically appears as a powder or solid with a color that can vary from pink to red, depending on its specific form and purity. It is generally insoluble in water but can dissolve in organic solvents. It is relatively stable under normal conditions but should be handled with care to avoid exposure to moisture, which can affect its stability.
- Chemical formula: C12H23ClO
- Molar mass: 218.77 g·mol−1
- Appearance: colorless liquid
- Density: 0.93 g/cm3
- Melting point: −17 °C (1 °F; 256 K)
- Boiling point: 145 °C (293 °F; 418 K) 18 torr
Occurrences and Applications
- In Industry: Cobalt laurate is used as a drying agent in paints, inks, and coatings. It helps to speed up the drying process of linseed oil and other oils used in these products.
- In Research: It is used in scientific research for studying the properties of metal soaps and their interactions with other substances.
- Synthetic Chemistry: It can be synthesized in a laboratory setting and is often used in chemical reactions where cobalt and lauric acid are required.
- Natural Occurrences: It does not occur naturally in its pure form. It is typically synthesized for specific applications rather than being found in nature.